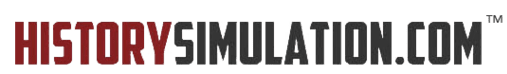SOCIAL STUDIES CONCEPTS
Teaching With Concepts
Every History topic is centered around a few concepts. When students learn and understand History Concepts they are able apply those concepts to other topics and develop a deeper understanding of why historical events happened
Topics Vs. Concepts
Topic: Is a specific event, era or subject in history.
Concept: is something that is timeless and transferable.
-Not specific to any particular topic
-Can be applied to many different topics or subjects
Email Mr. Harms directly to join a specific email list that receives all new Concept Graphics that are created.
SOCIAL STUDIES CONCEPTS AND DESCRIPTIONS
Each of the Social Studies Concepts is linked to a graphic that explains it with a short example video. Click on the Concept to see a graphic explaining the concept. Click on the example video to see a video explaining the graphic.
History Concepts

Balance: When power is equal on both sides.

Change:To make or become different.
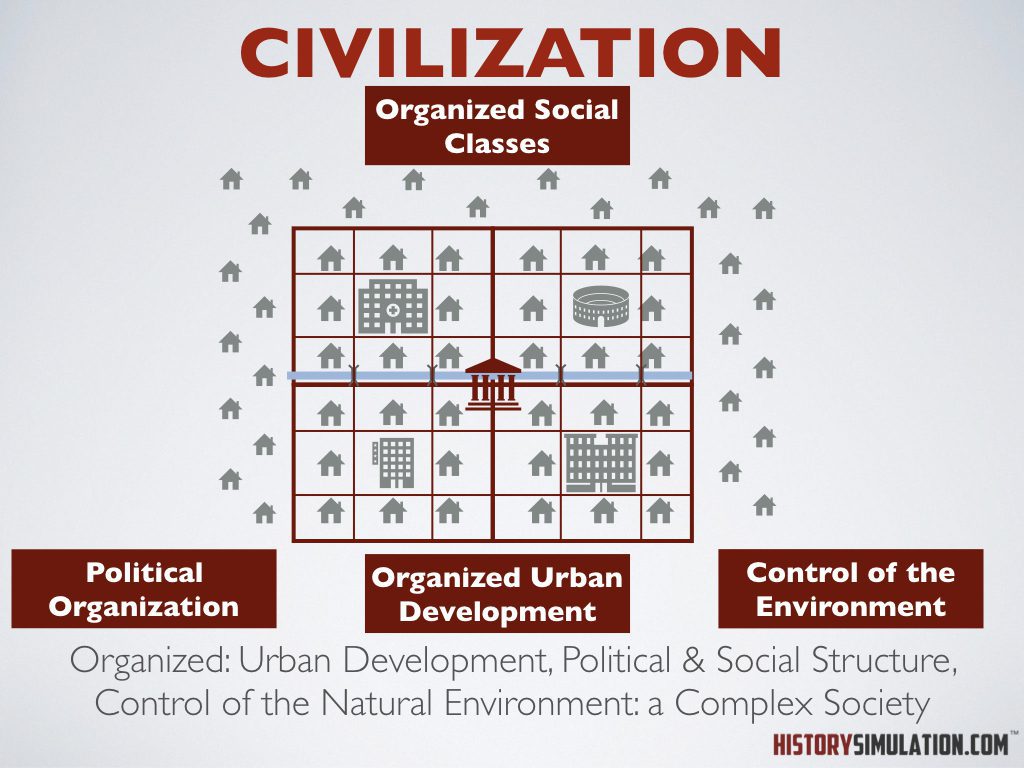
Civilization: Organized: Urban Development, Political & Social Structure, Control of the Natural Environment: a Complex Society.

Colonialism: The policy or practice of acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers and exploiting it economically.
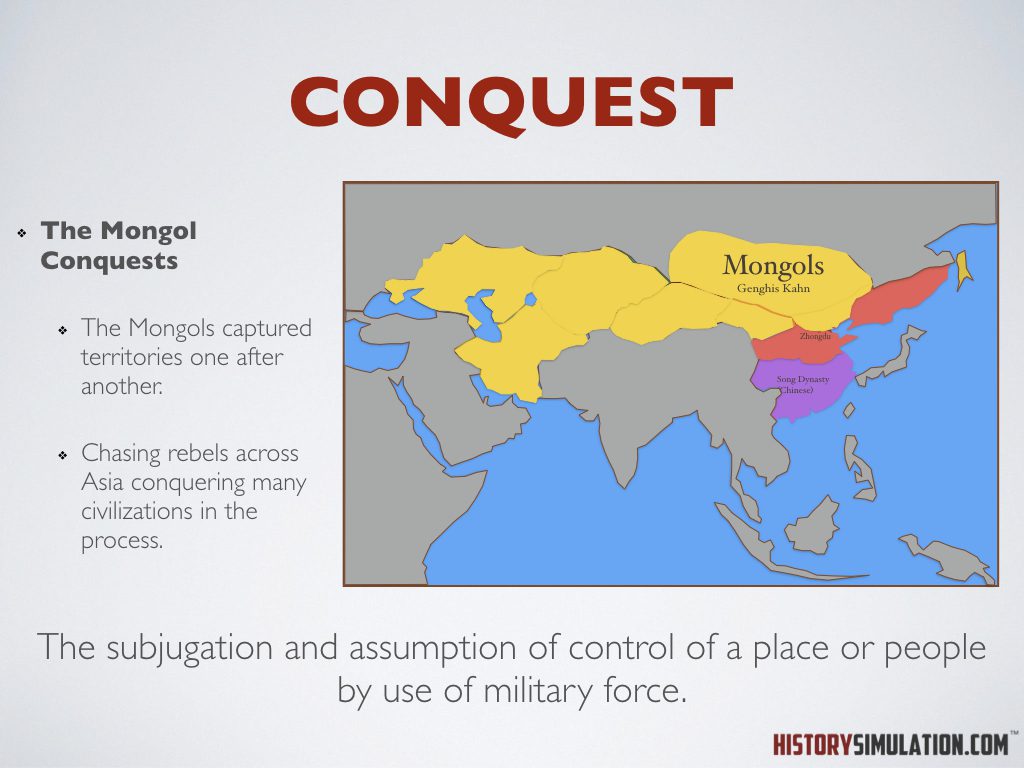
Conquest: The subjugation and assumption of control of a place or people by use of military force.

Consequence: The intended or unintended result of an action or decision.

Conflict: A disagreement, sometimes un-reconcilable, that may lead to aggressive military behavior.
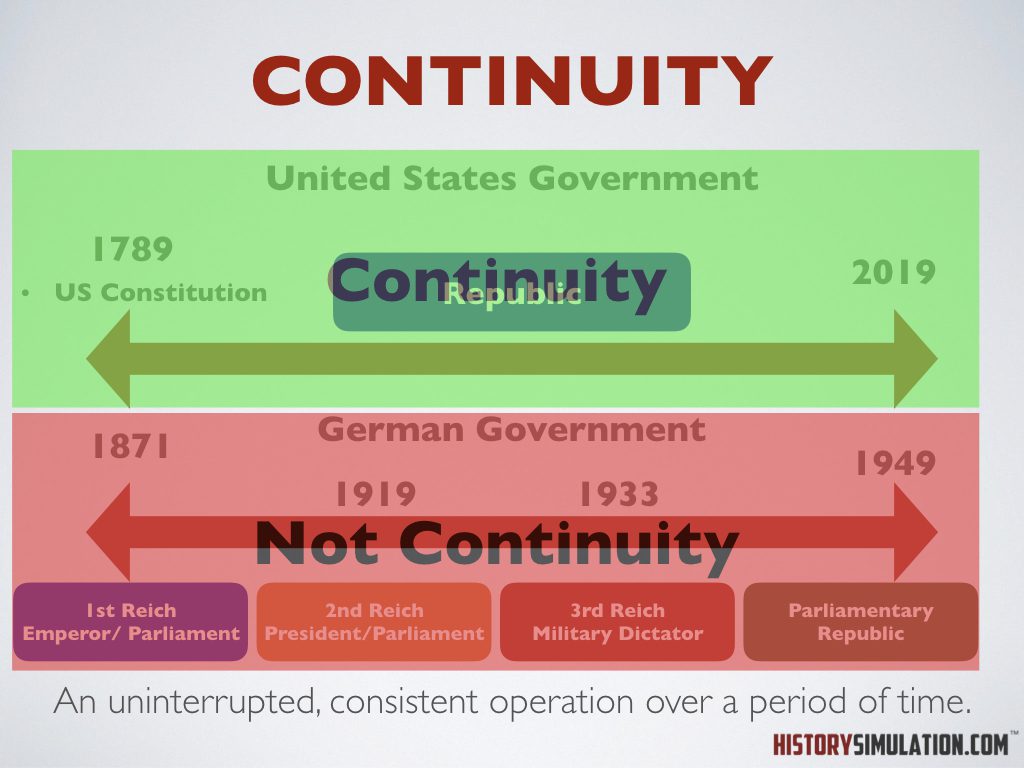

Culture: Traditions, customs or way of life of a community.

Era: A long and distinct period of history with a particular feature or characteristic.

Escalation: An increase in the intensity or seriousness of a situation leading to a larger crisis.
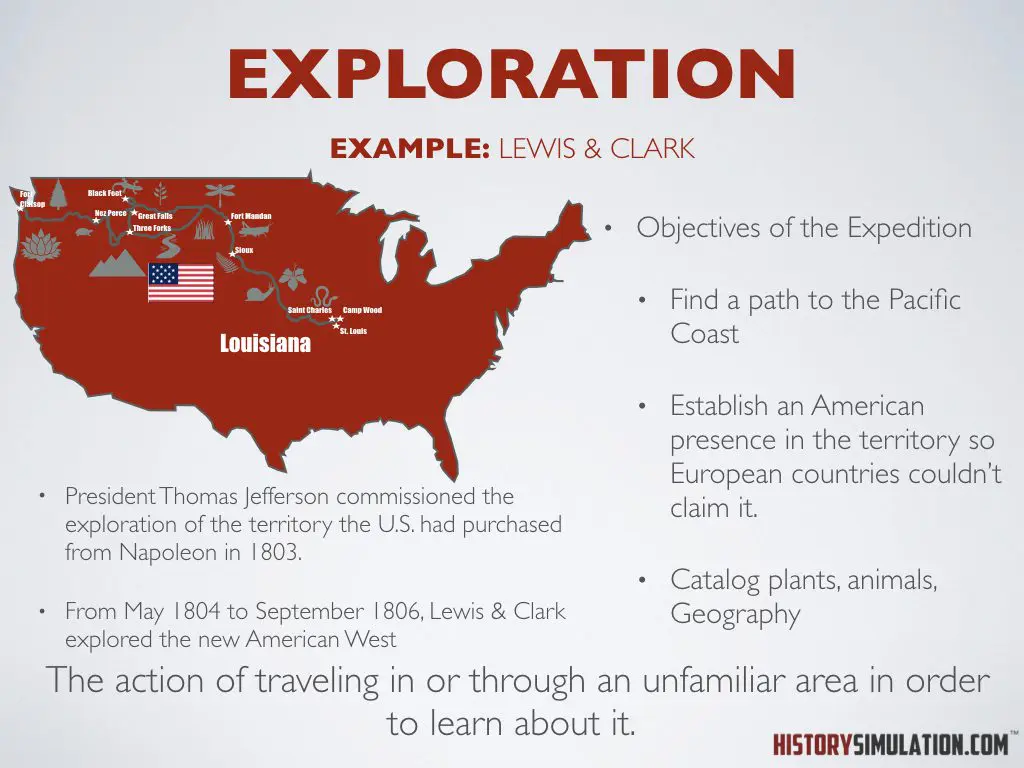
Exploration: The action of traveling in or through an unfamiliar area in order to learn about it.

Identity: The values, culture and traditions that an individual or group of people identify with.
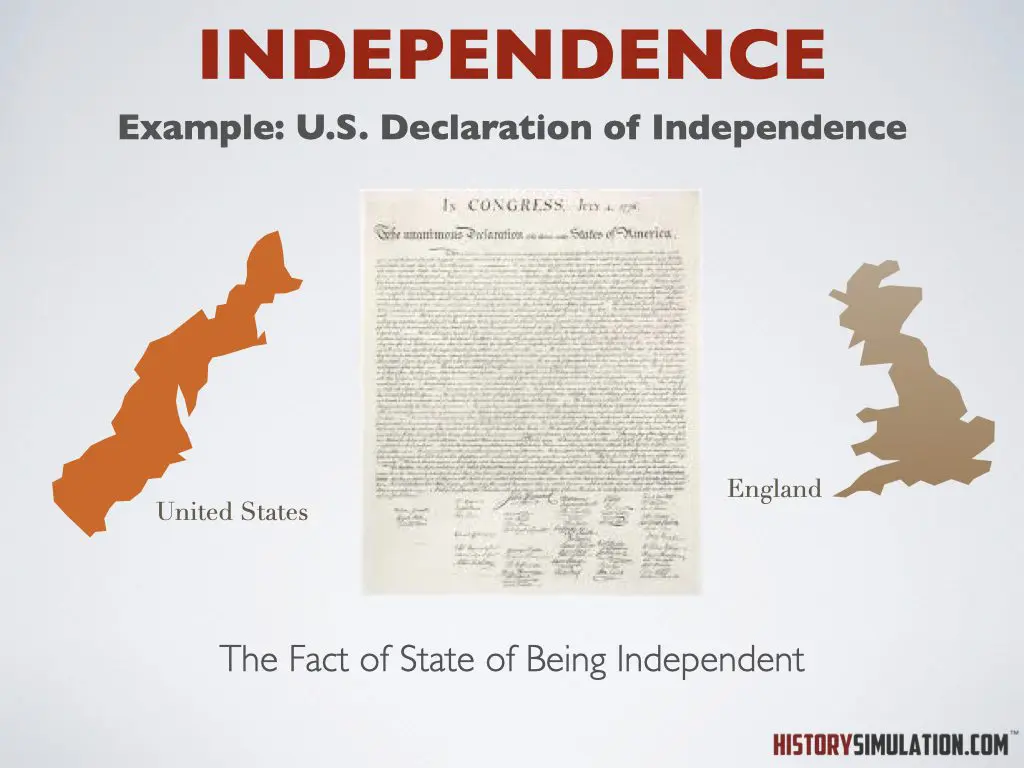
Independence: The fact or state of being independent.

Innovation: Innovation is the act of improving something or creating something that is a new technology.
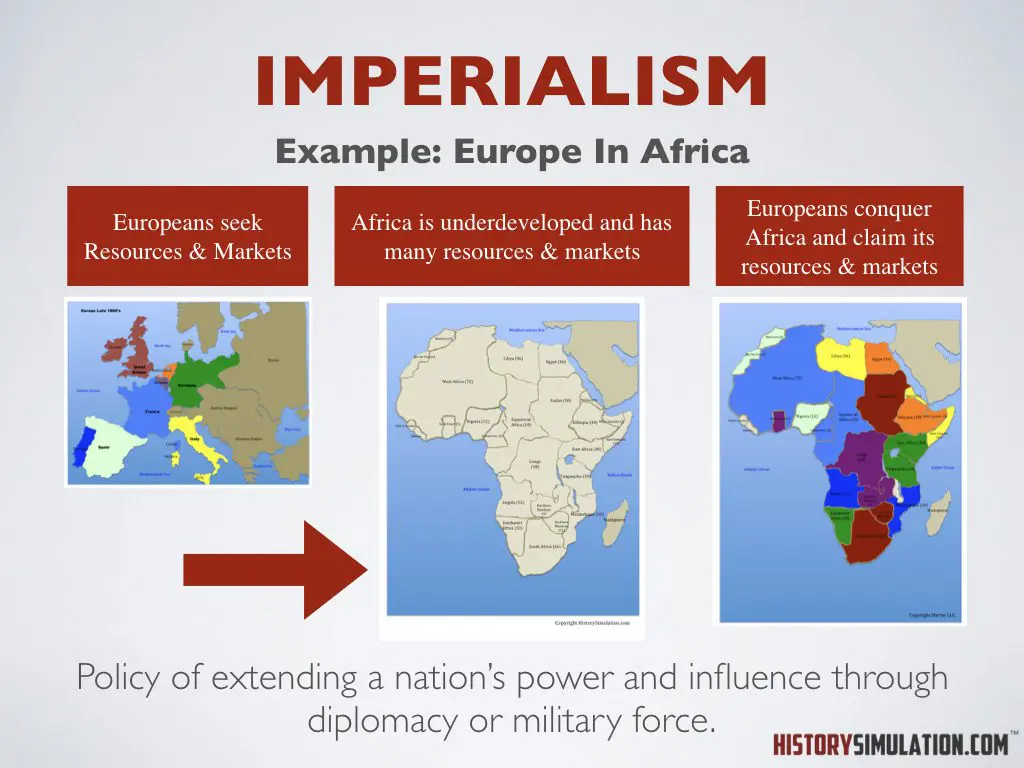
Imperialism: The policy of extending a nation's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
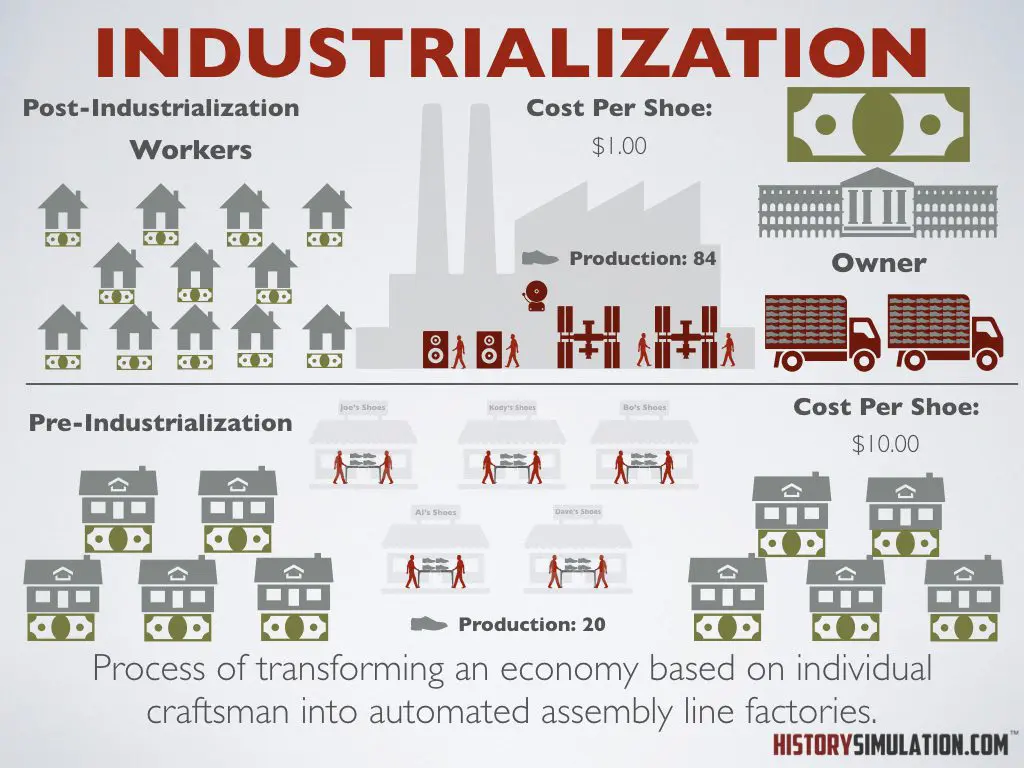
Industrialization: Process of transforming an economy based on individual craftsman into automated assembly line factories.
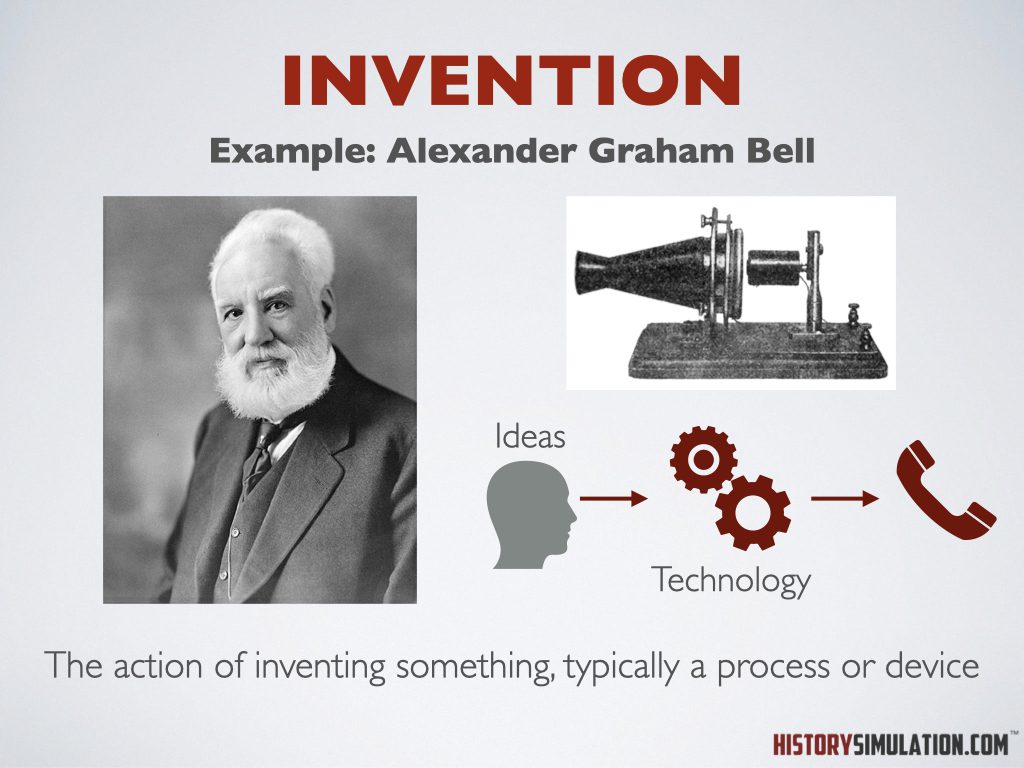
Invention: The action of inventing something, typically a process or device
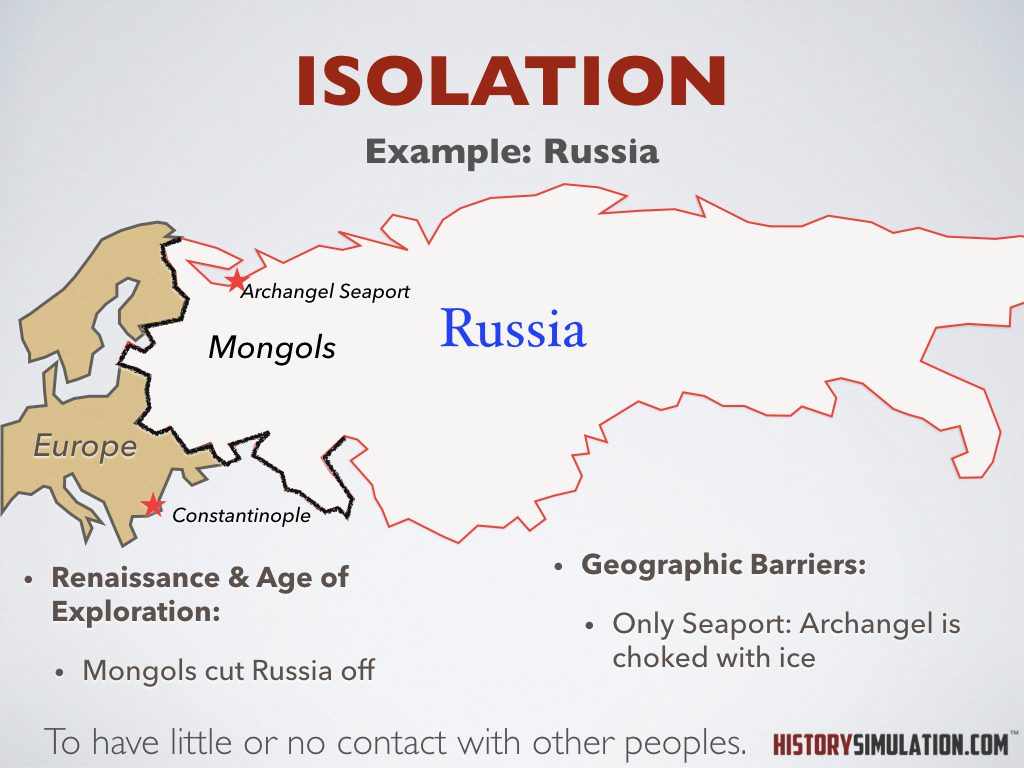
Isolation: To have little or no contact with other peoples.
Example Video
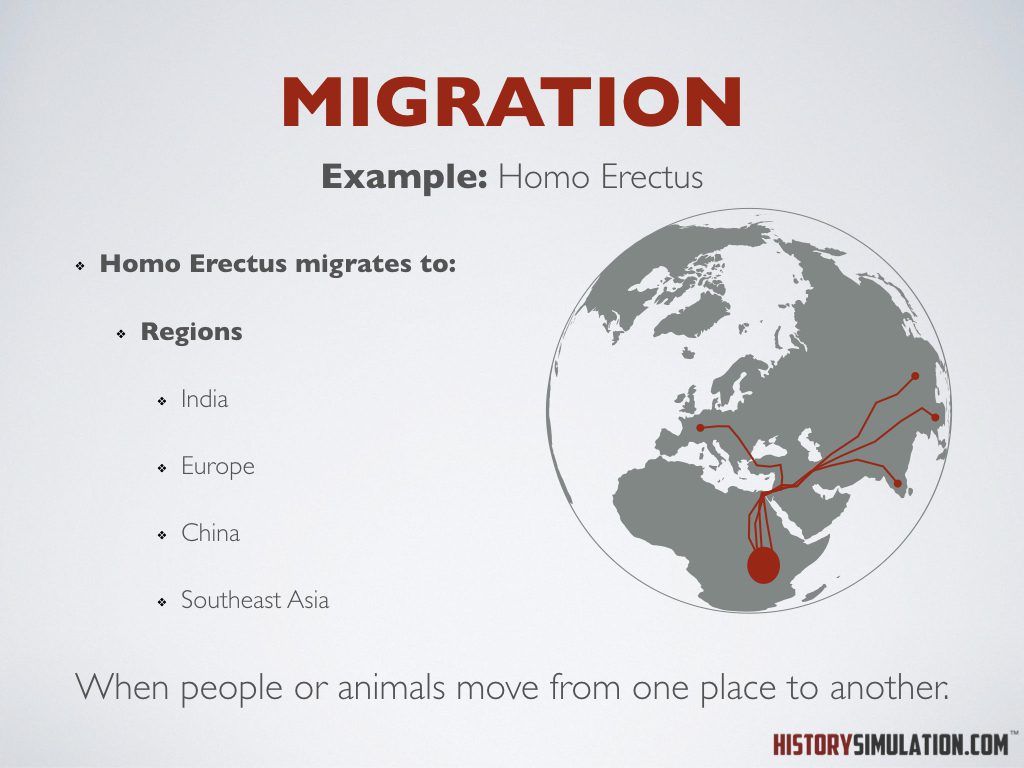
Migration: When people or animals move from one place to another.

Militarism: Policy of glorifying military power and being prepared for war.

Nationalism: A sentiment or sense of belonging or pride in your country
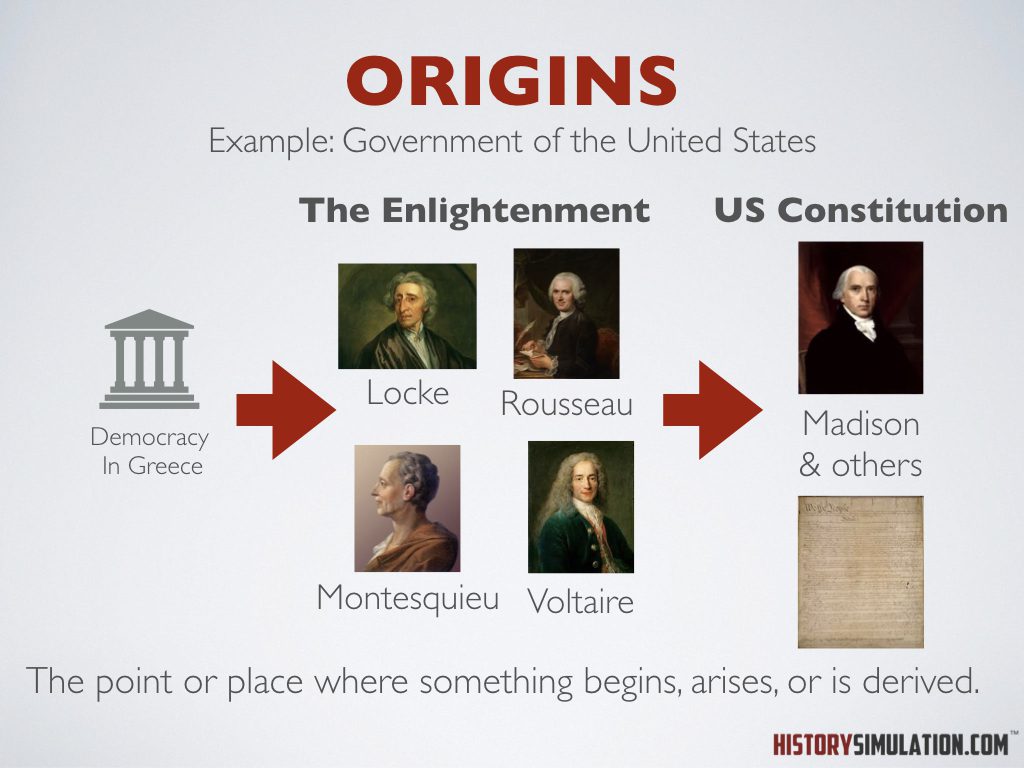
Origins: The point or place where something begins, arises, or is derived.
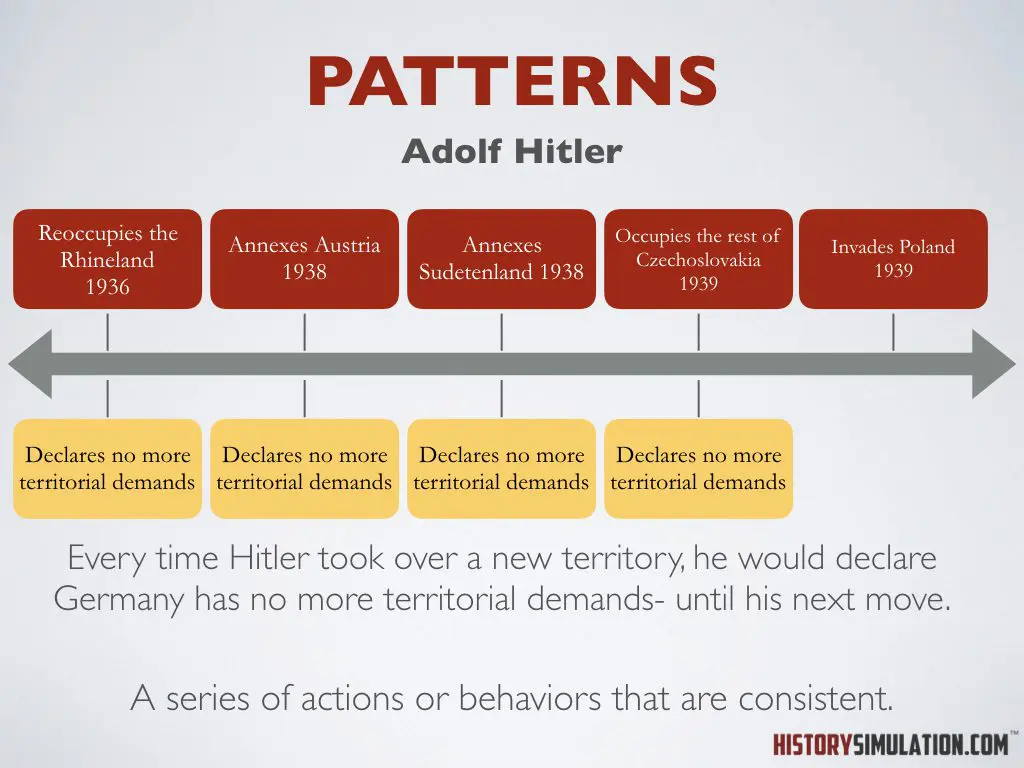
Patterns: A series of actions or behaviors that are consistent.

Progressivism: Political philosophy based on social reform through advancements in science, technology, economic development and social organization.
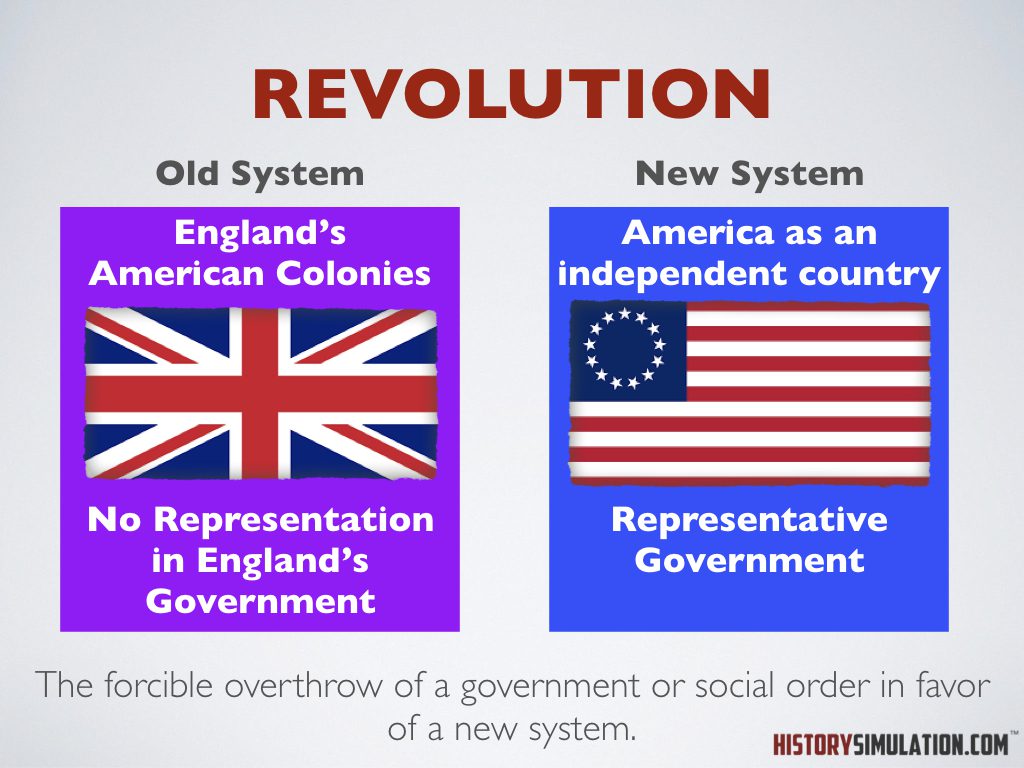
Revolution: The forceable overthrow of a government or social order in favor of a new system.

Sectionalism: Narrowing your interest to more local/state/regional issues- disregarding the overall good of the state or nation.
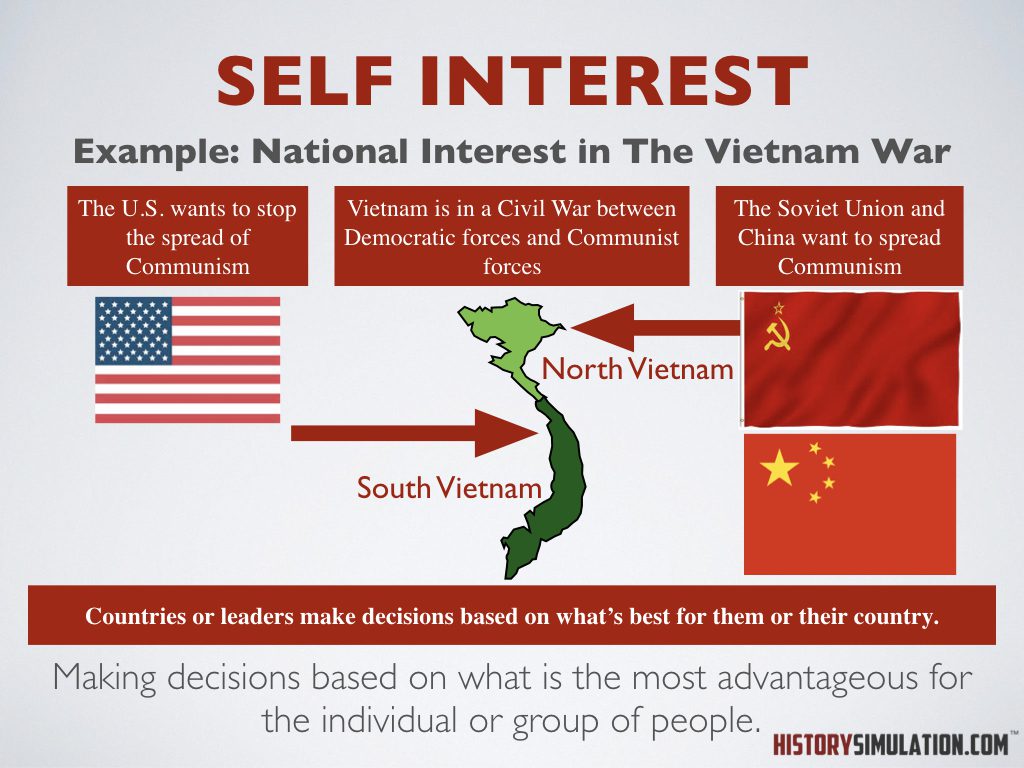
Self-Interest: Making decisions based on what is the most advantageous for the individual or group of people.
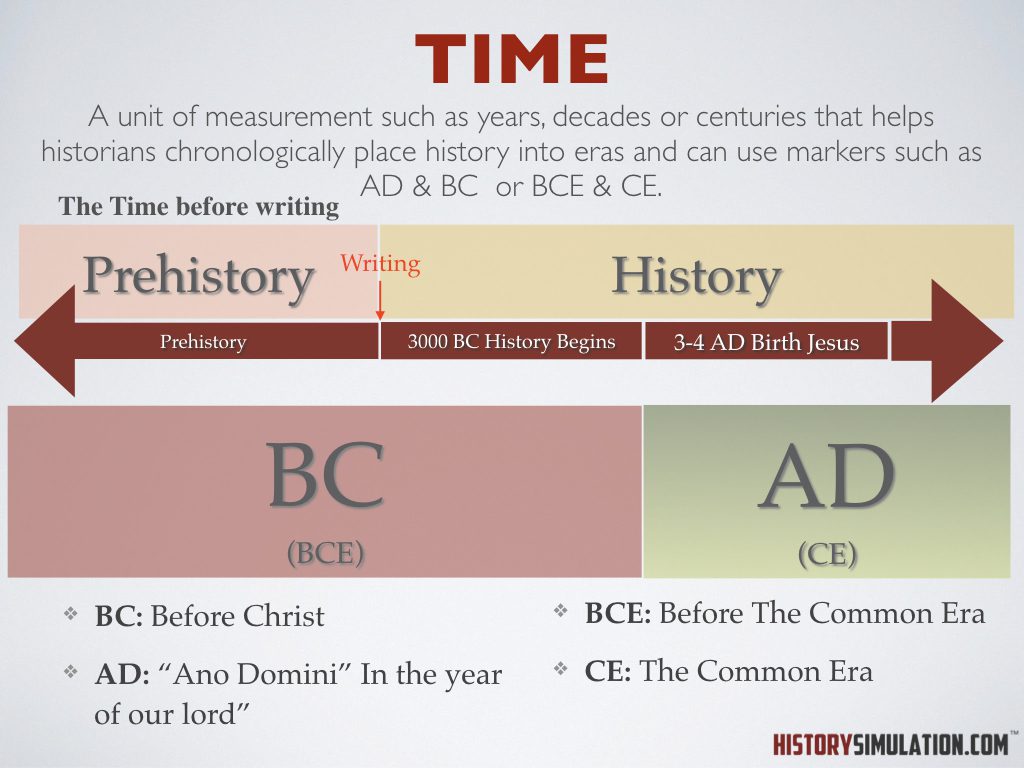
Time: a unit of measurement such as years, decades or centuries that help historians chronologically place history into eras and can use markers such as AD & BC or BCE & CE.
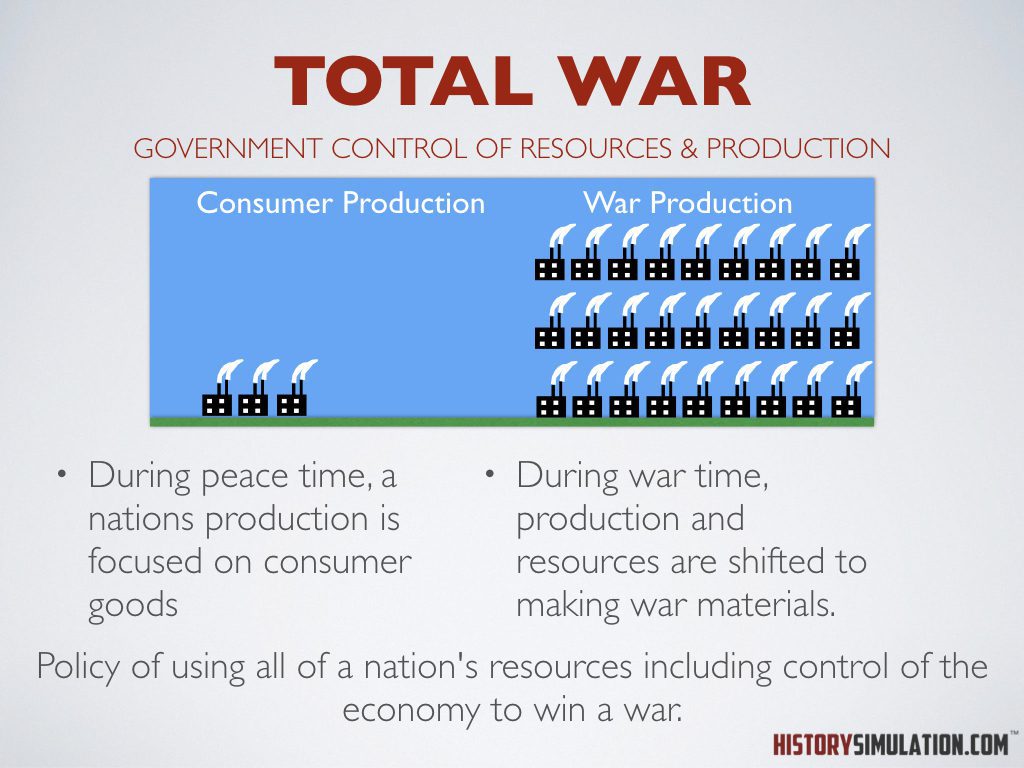
Total War: Policy of using all of a nation's resources including control of the economy to win a war.
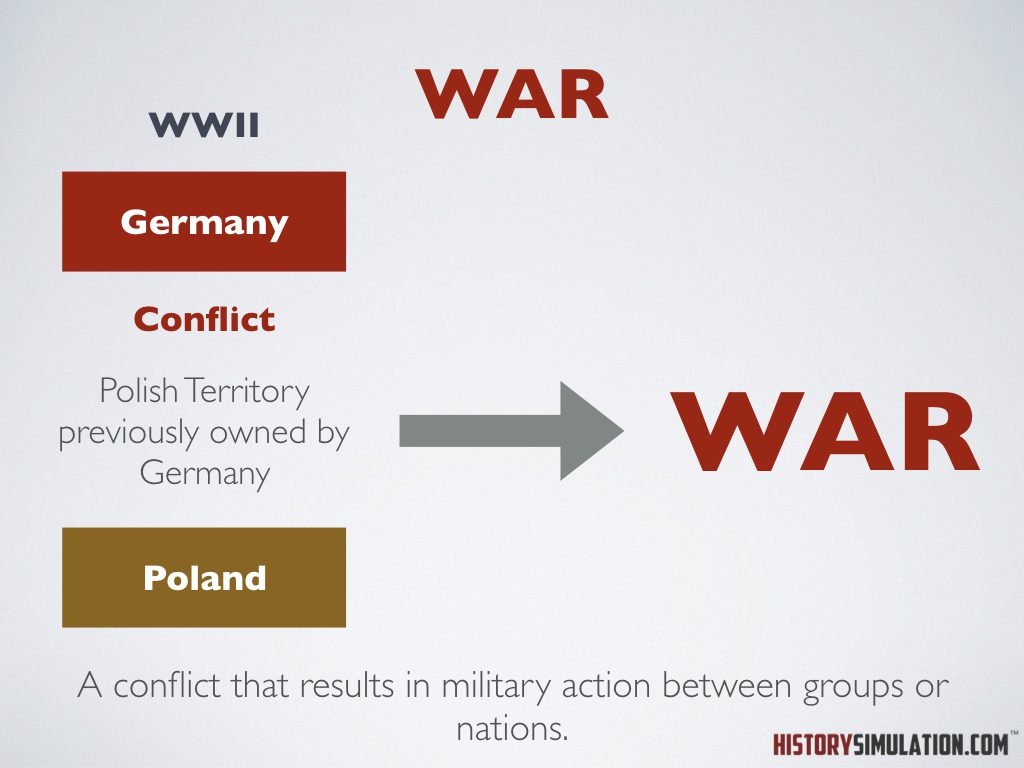
War: A conflict that results in military action between groups or nations.

Tolerance: The ability to live with beliefs or behaviors that one does not agree with.
Global Connections Concepts
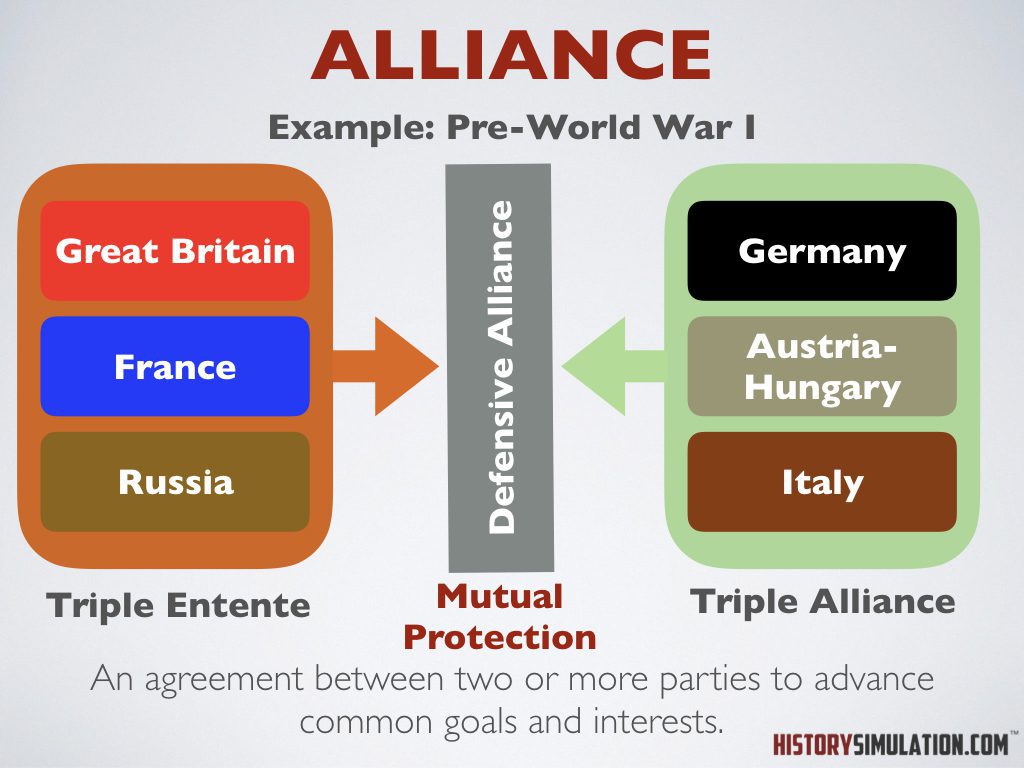
Alliance: An agreement between two or more parties to advance common goals or interests.

Climate Change: A change in global or regional climate patterns attributed largely to the increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide produced by the use of fossil fuels.
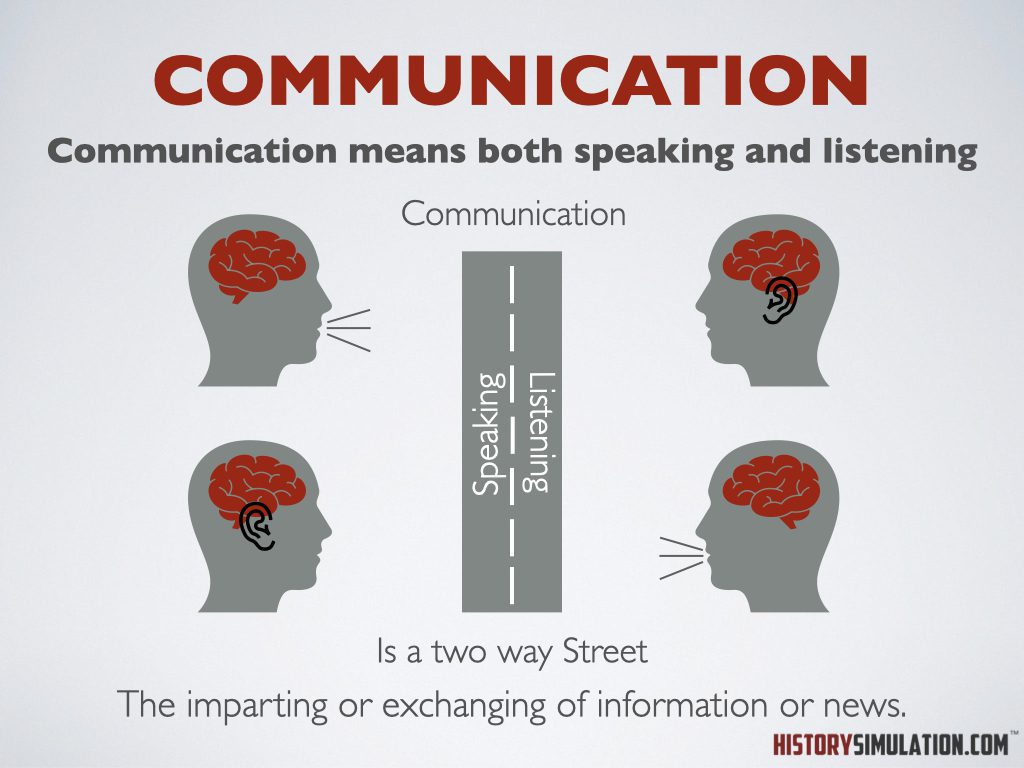
Communication: The imparting or exchanging of information or news.
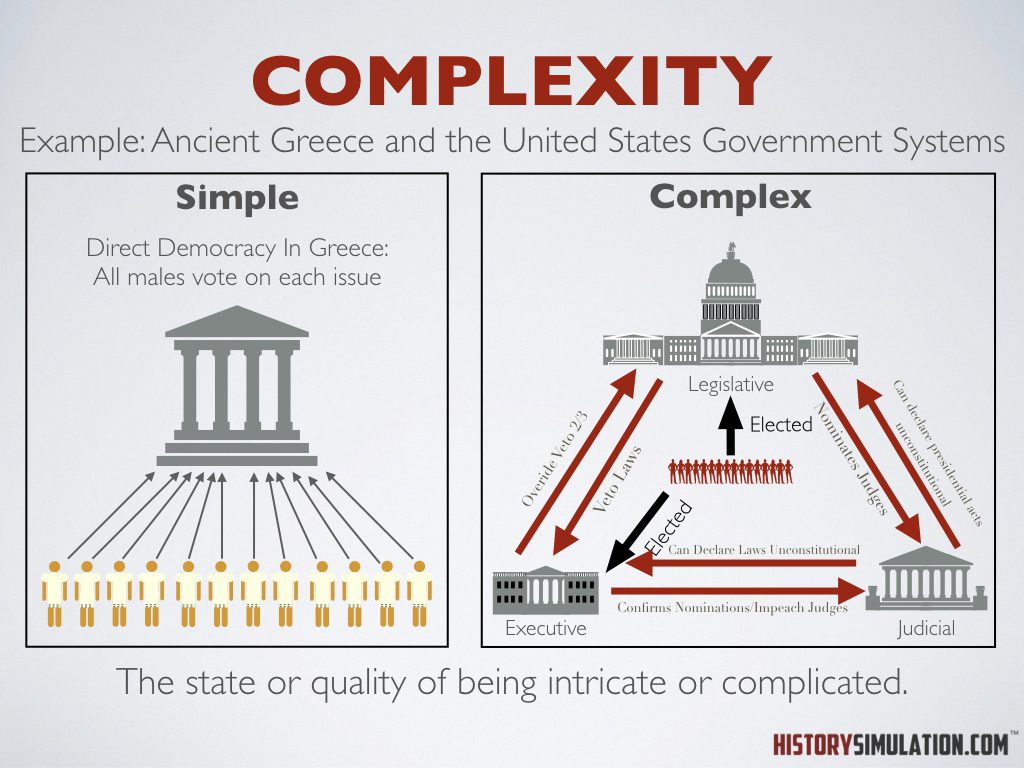
Complexity: The state or quality of being intricate or complicated.
Example Video

Cooperation: The process of working together to achieve a common outcome.
Example Video

Crisis: A time of intense difficulty, trouble, or danger.

Diffusion: When culture, goods or ideas are mixed together and can result in blending and innovation.
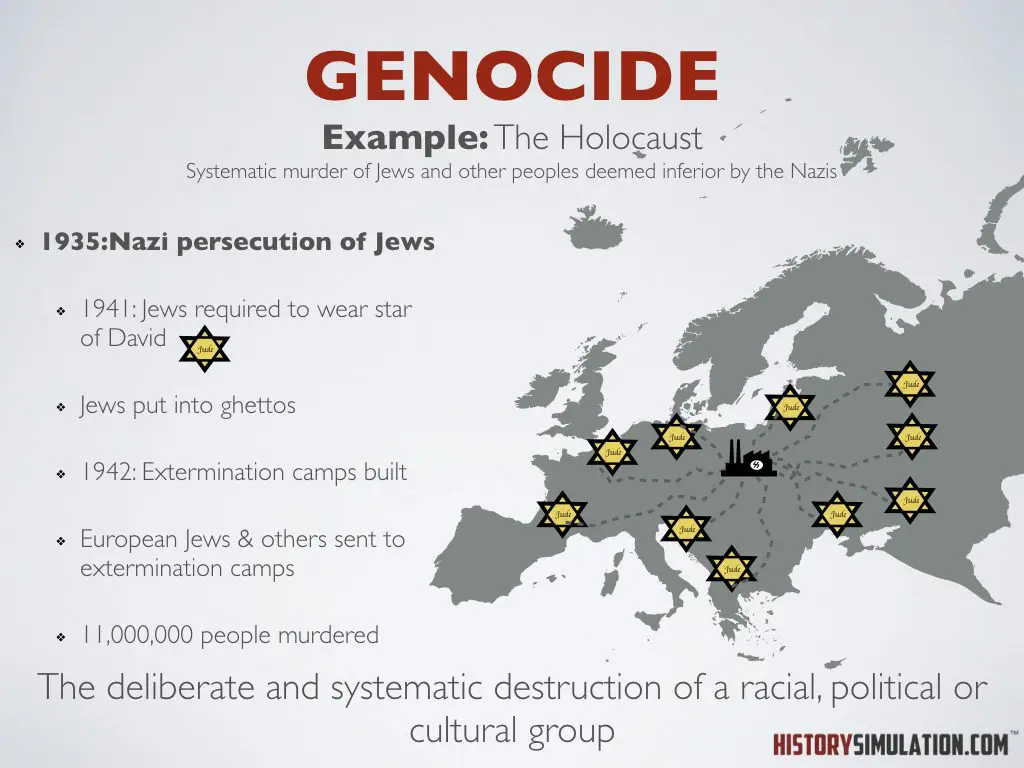
Genocide: The deliberate and systematic destruction of a racial, political or cultural group.
Example Video

Global Economy: The International Exchange of Goods and Services

Human Rights: Human rights include the right to life and liberty, freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to work and education, and many more.

International Law: A body of rules established by custom or treaty and recognized by nations as binding in their relations with one another.
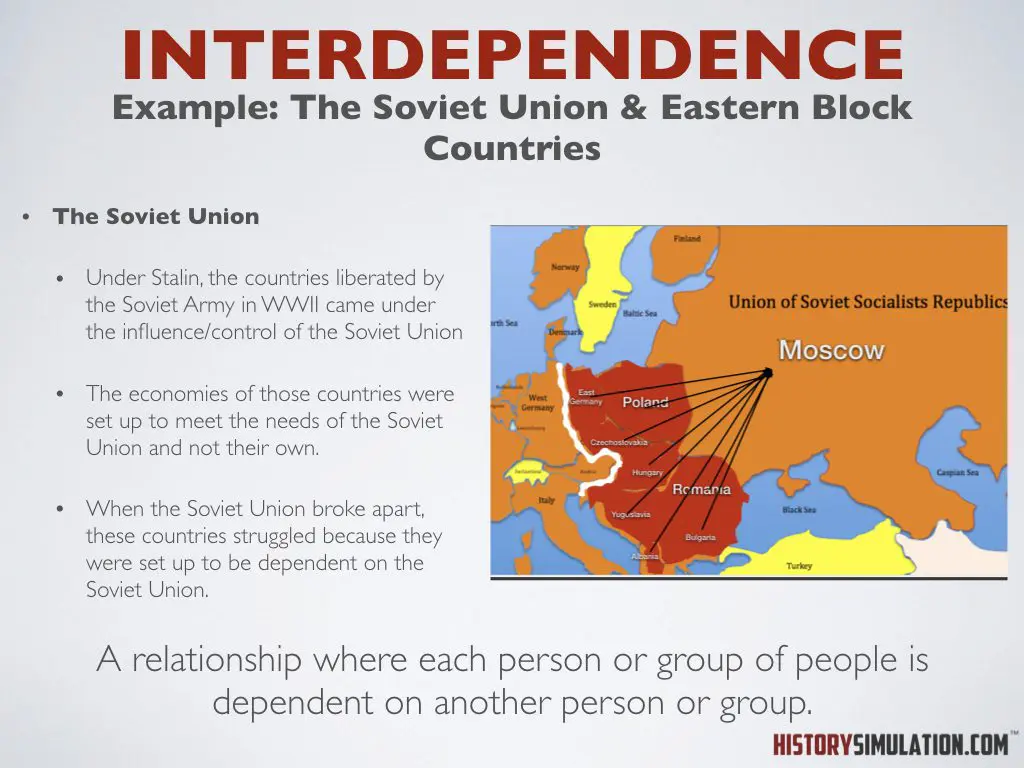
Interdependence: A relationship where each person or group of people is dependent on another person or group.
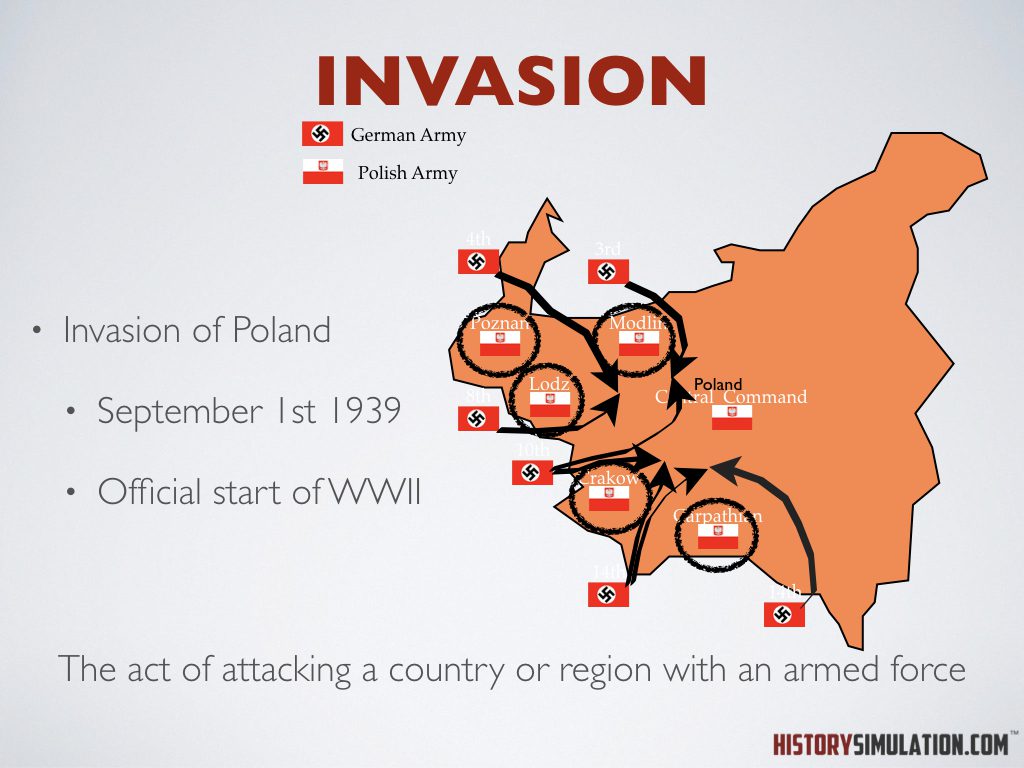
Invasion: The act of attacking a country or region with an armed force.
Example Video

Peace: The absence of conflict or war.

System: A set of things working together as parts of a mechanism or an interconnecting network

Terrorism: the unlawful use of violence and intimidation, especially against civilians, in the pursuit of political aims.
Geography Concepts
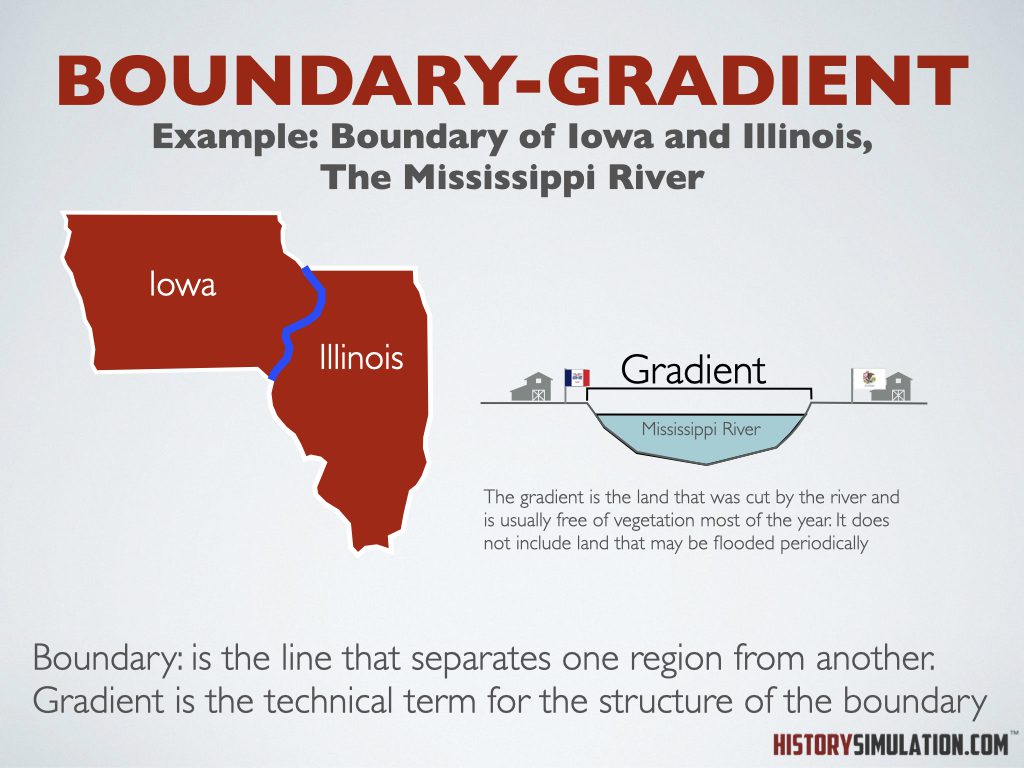
Boundary/Gradient: Boundary: is the line that separates one region from another. Gradient is the technical term for the structure of the boundary.
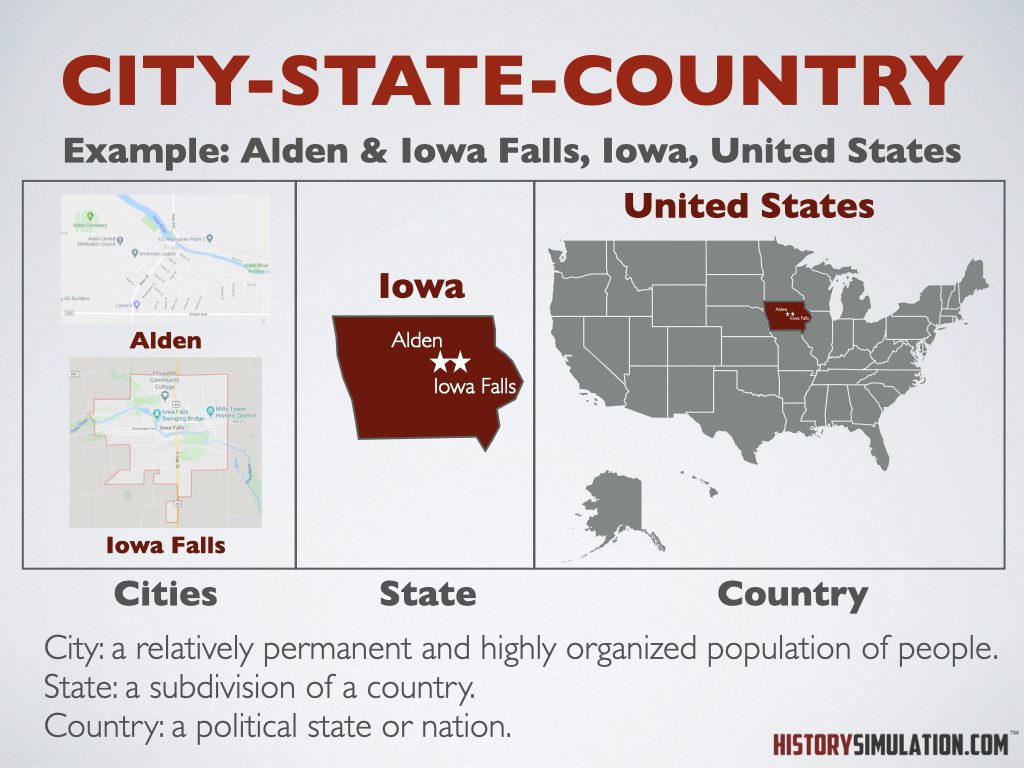
City-State-Country: City: a relatively permanent and highly organized population of people. State: a subdivision of a country. Country: a political state or nation.
Climate: The long term pattern of weather in a particular area.
Connections: Relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space.
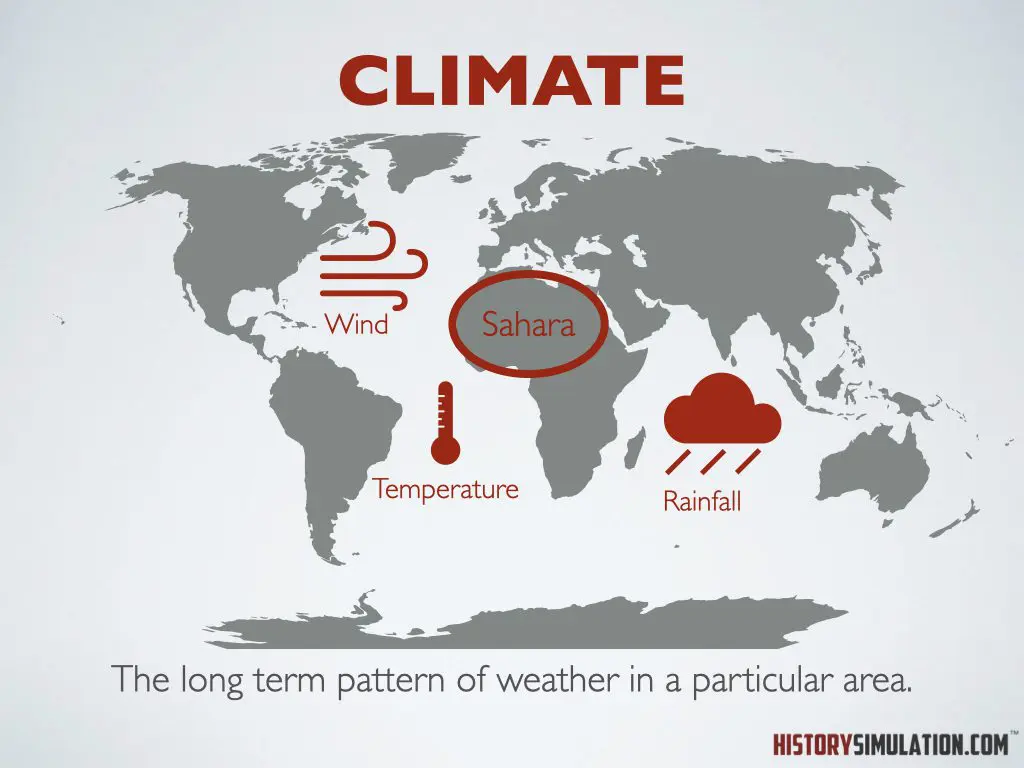
Distribution: The natural arrangement and apportionment of the various forms of animals and plants in the different regions and localities of the earth.
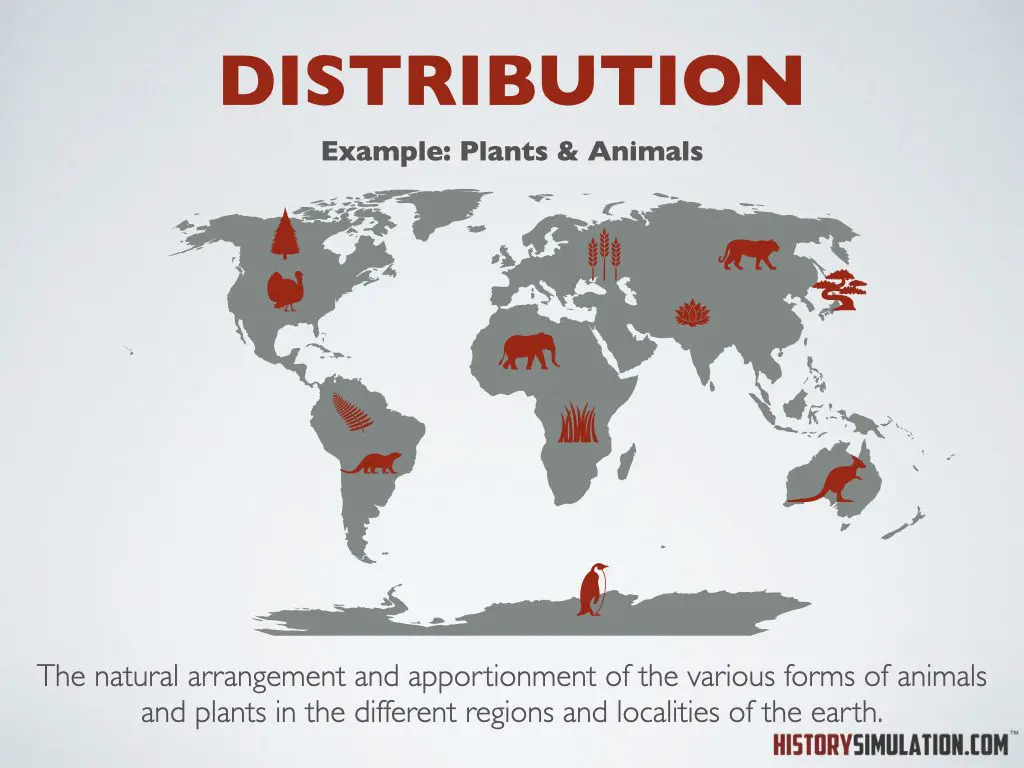
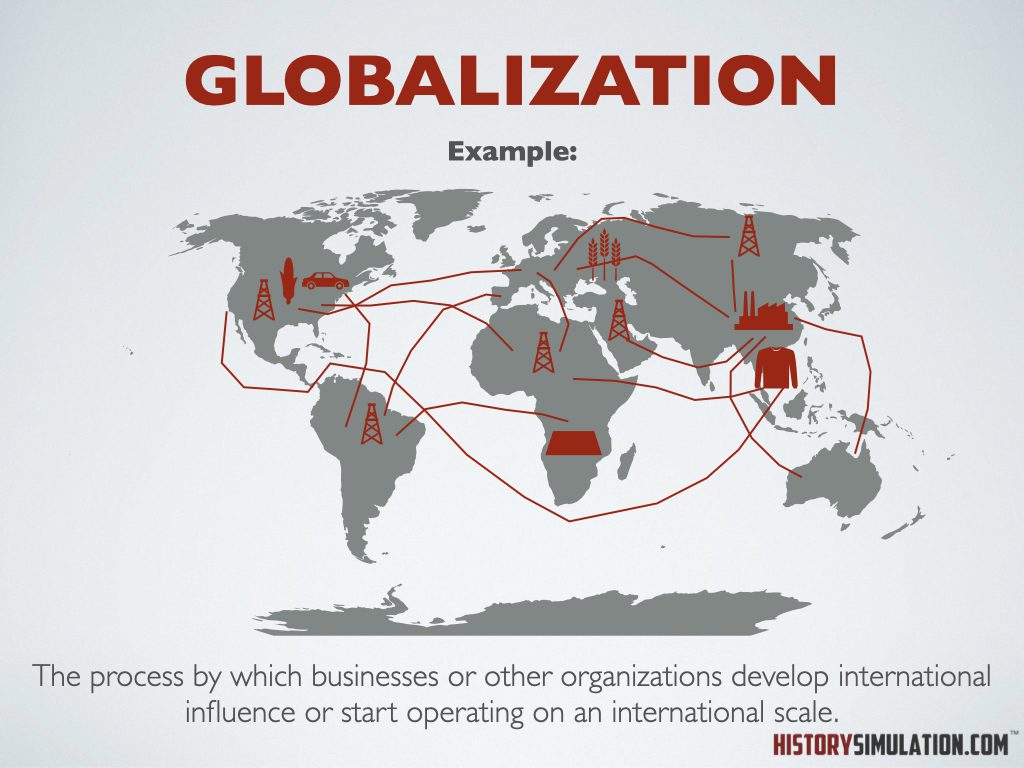
Globalization: The process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale.
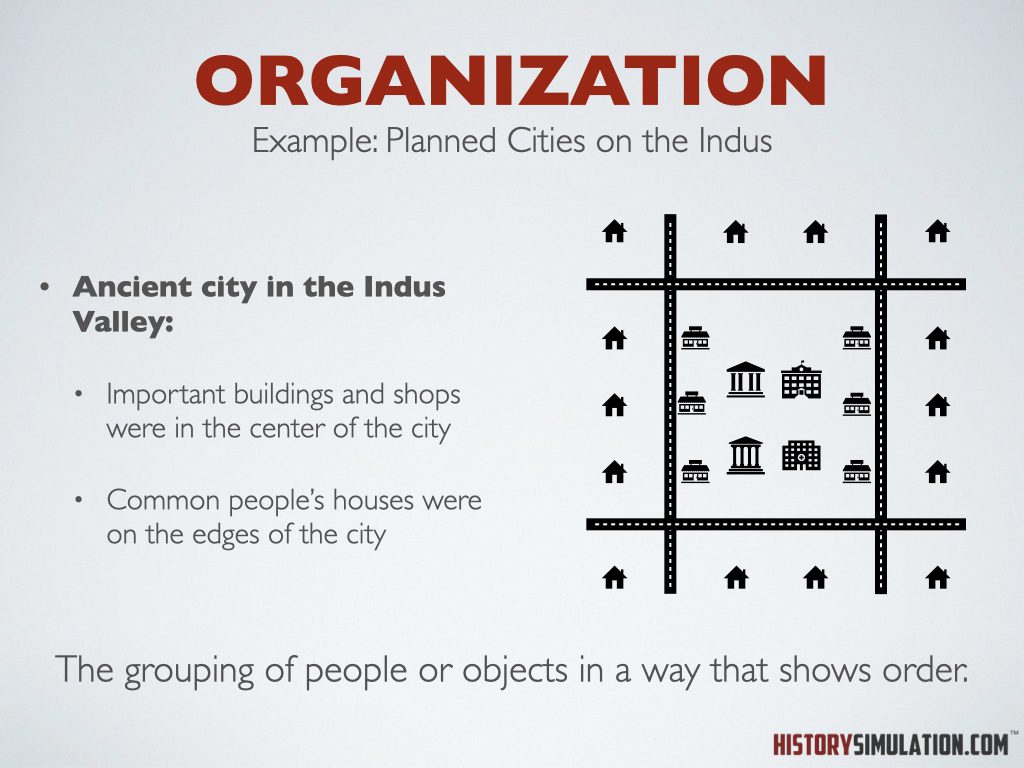
Organization: -The grouping of people or objects in a way that shows order.
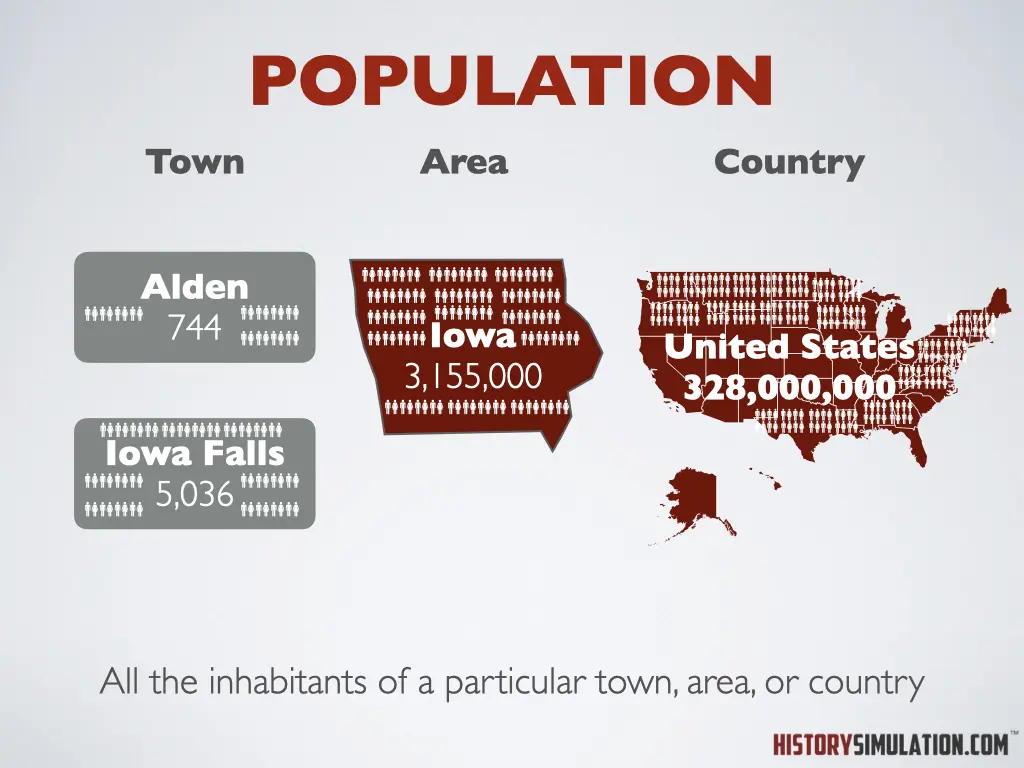
Population: All the inhabitants of a particular town, area, or country
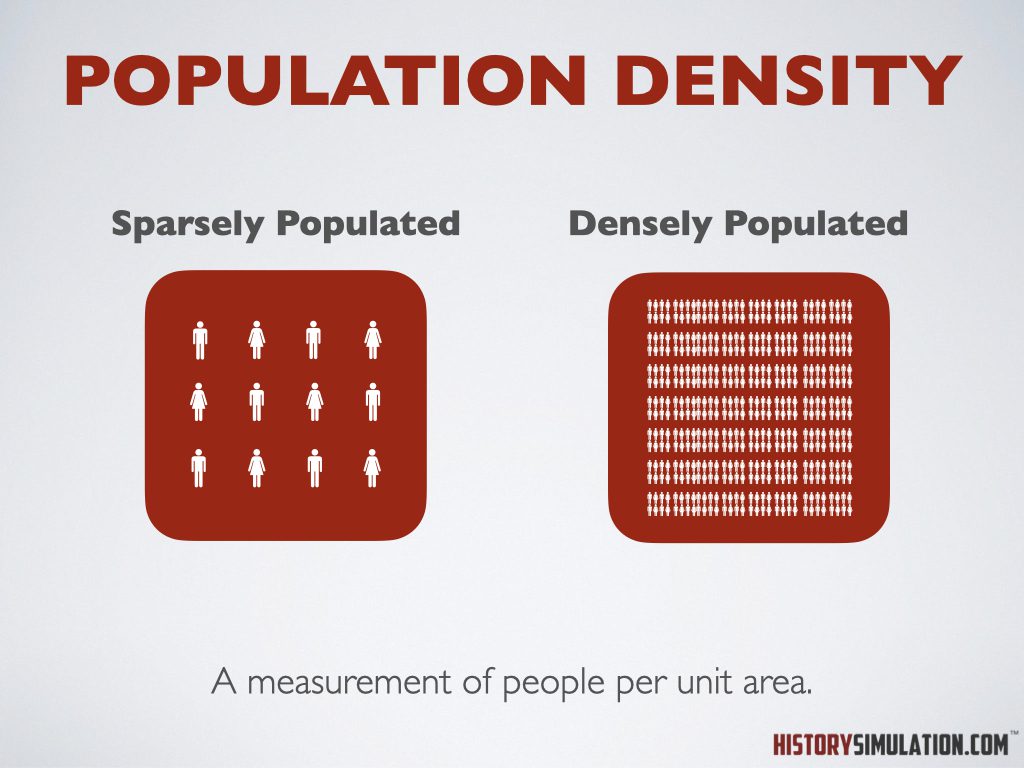
Population Density: A measurement of people per unit area.
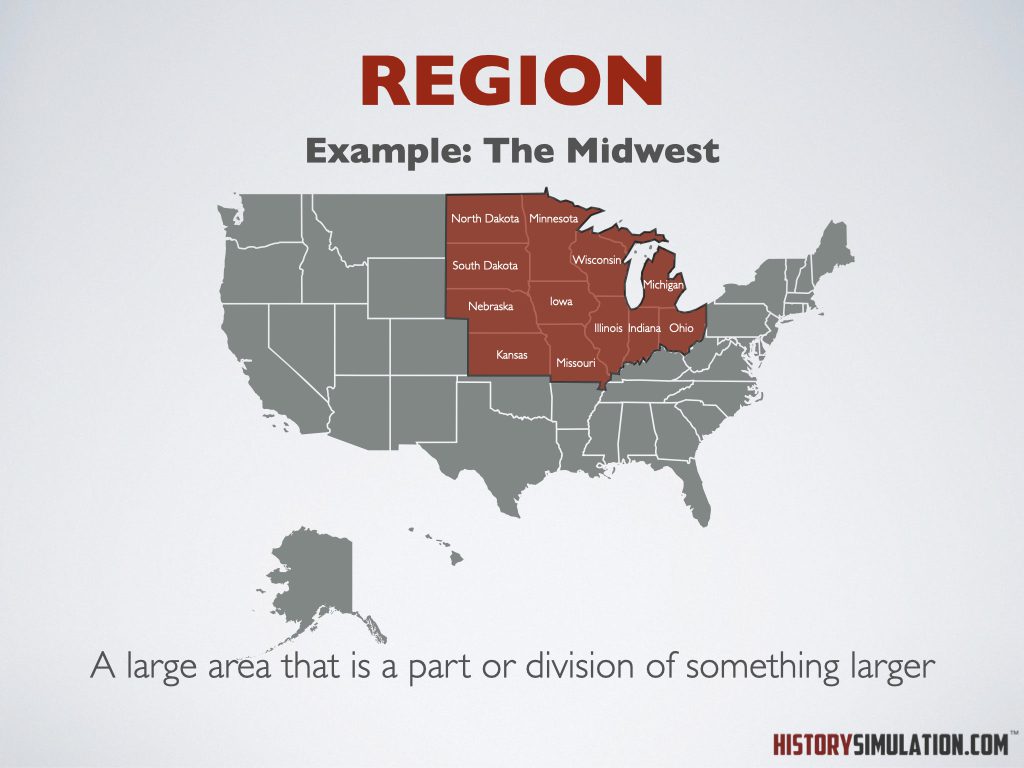
Region: A large area that is a part or division of something larger
Religion: A system of beliefs, symbols and rituals, that guide human behavior; gives meaning to life and unites believers into a community.
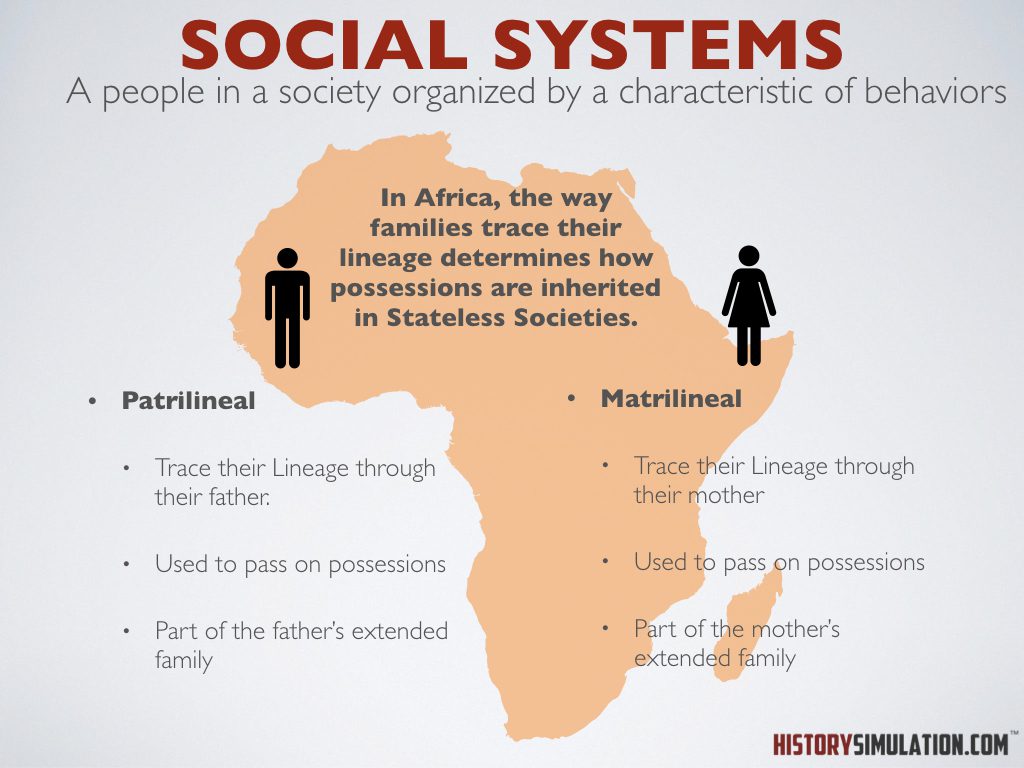
Social Systems: A people in a society organized by a characteristic of behaviors.
Values & Beliefs: Shared beliefs about what is good-bad, right-wrong, or desirable-undesirable / specific statements that people hold to be true.
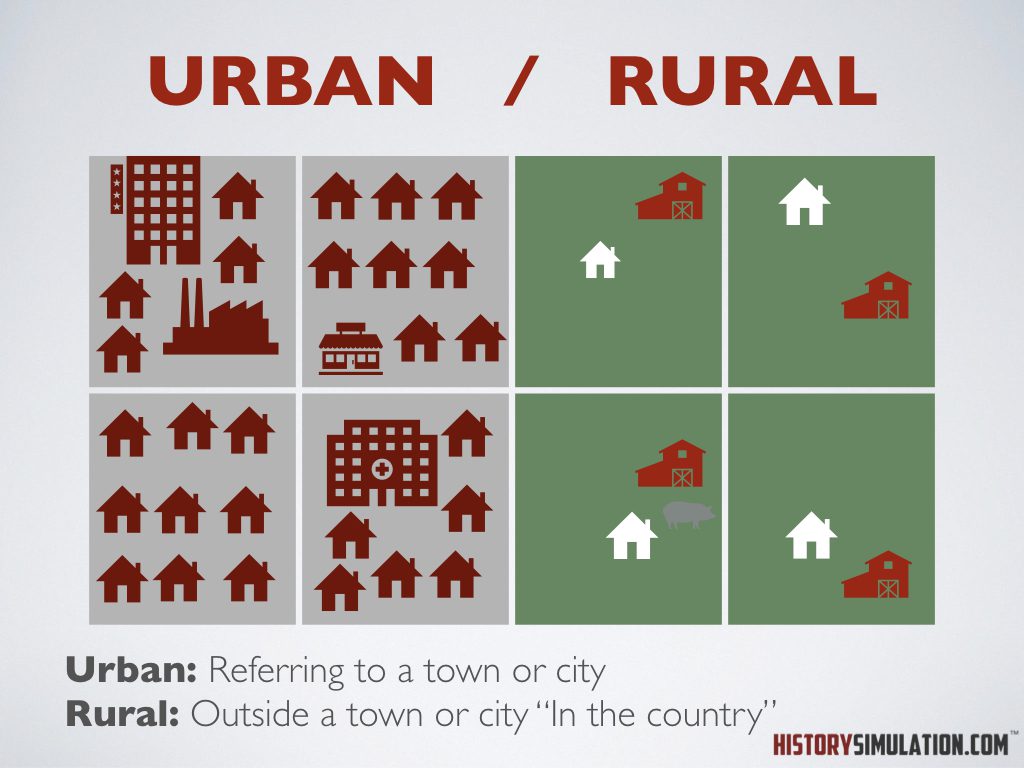
Urban/Rural: Urban: Referring to a town or city.
Rural: Outside a town or city “In the country”
Government Concepts
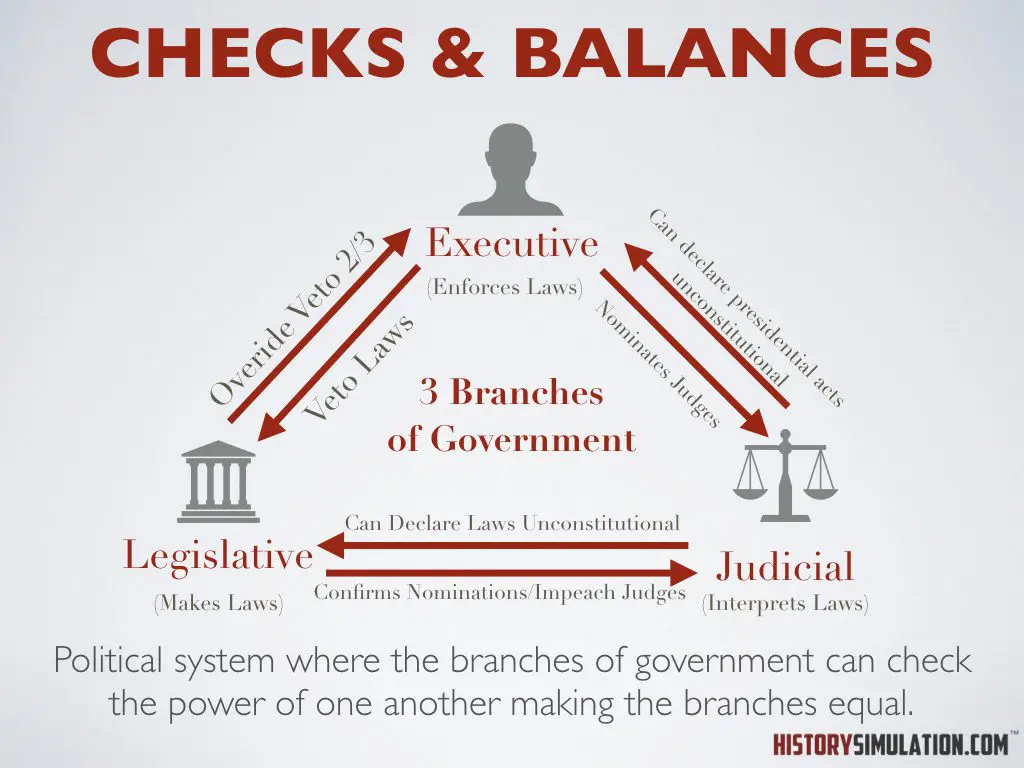
Checks & Balances: Political system where the branches of government can check the power of one another making the branches equal.
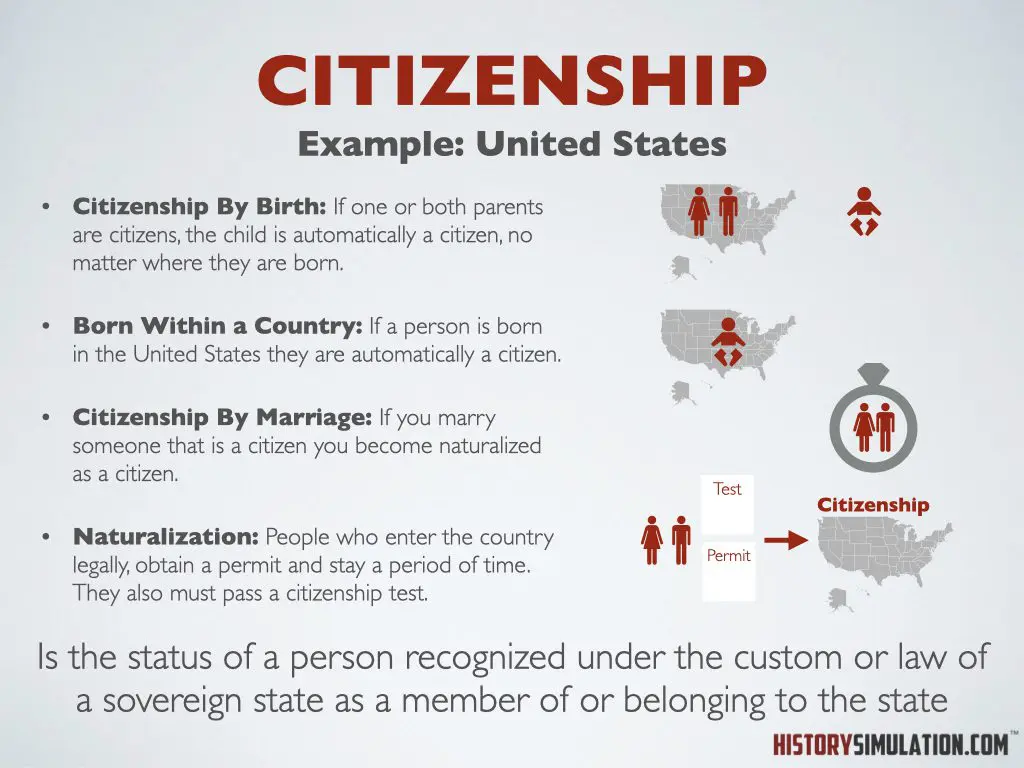
Citizenship: Is the status of a person recognized under the custom or law of a sovereign state as a member of or belonging to the state
Civic Engagement: Individual and collective actions designed to identify and address issues of public concern

Communism: A way of organizing society in which the government owns the means of production and there is no private property.
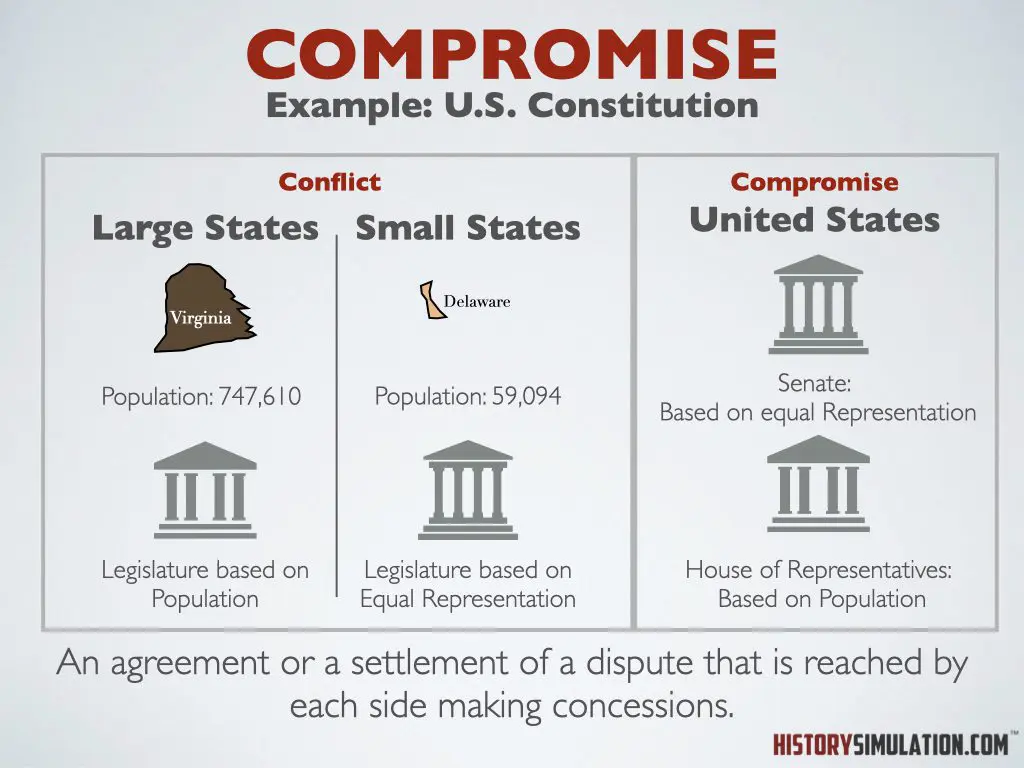
Compromise: An agreement or a settlement of a dispute that is reached by each side making concessions.
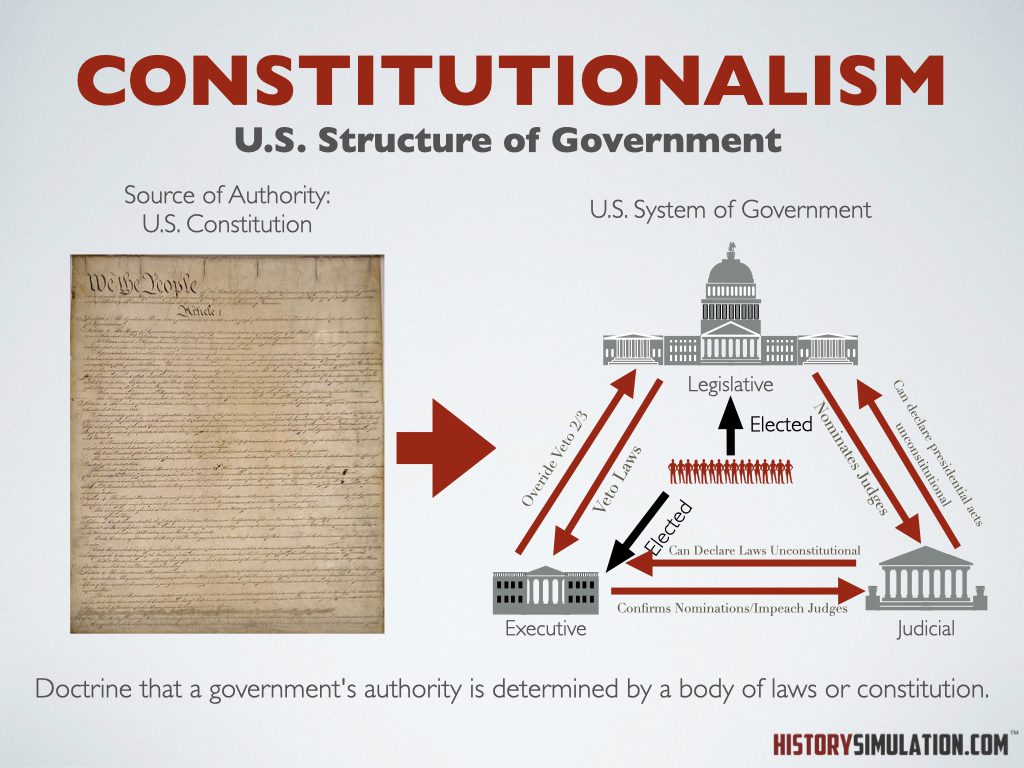
Constitutionalism: Doctrine that a government's authority is determined by a body of laws or constitution.

Democracy: A system of government by the whole population or all the eligible members of a state, typically through elected representatives
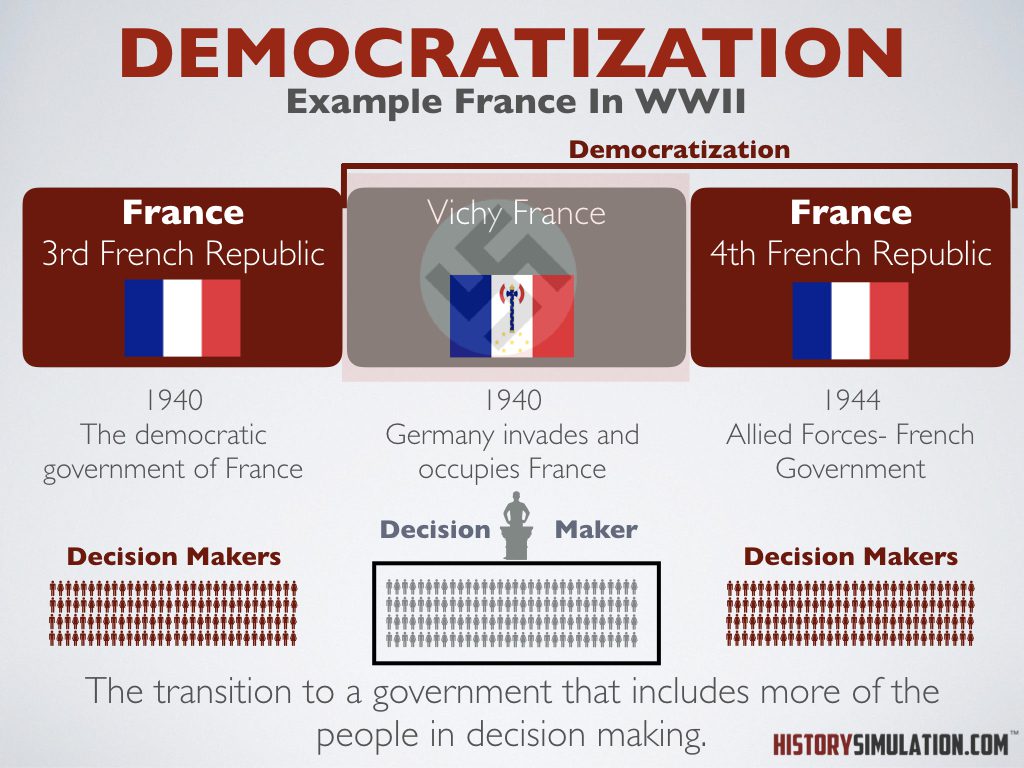
Democratization: The transition to a government that includes more of the people.

Diversity: The practice or quality of including or involving people from a range of different social and ethnic backgrounds and of different genders, etc
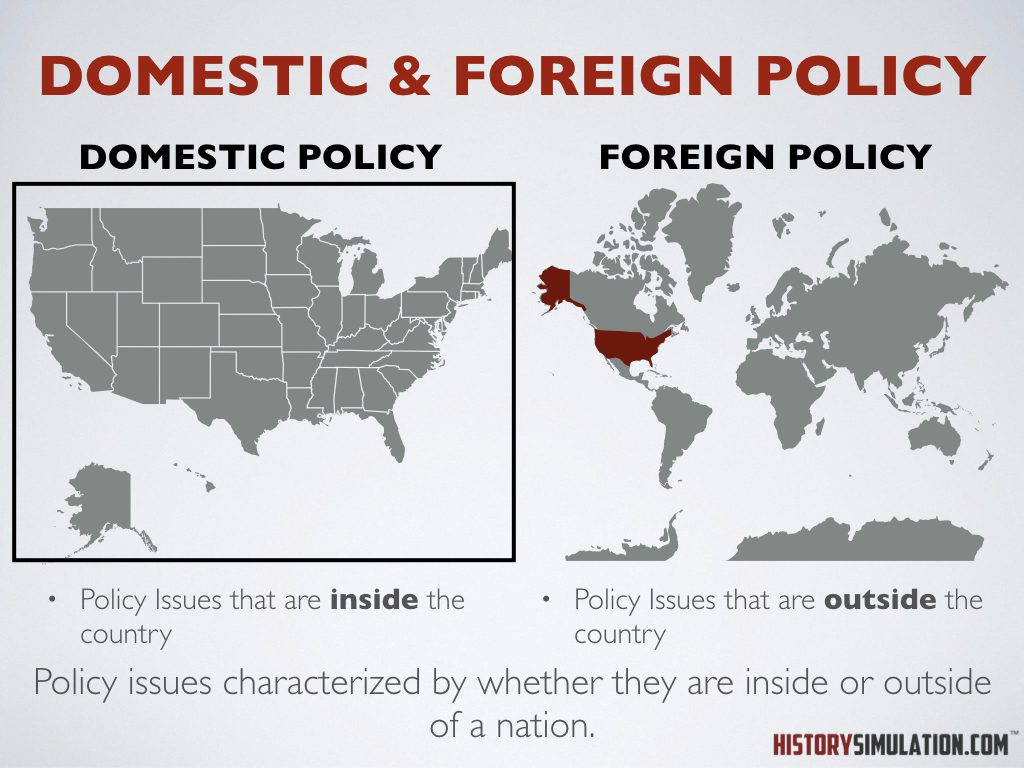
Domestic & Foreign Policy: Policy issues characterized by whether they are inside or outside of a nation.
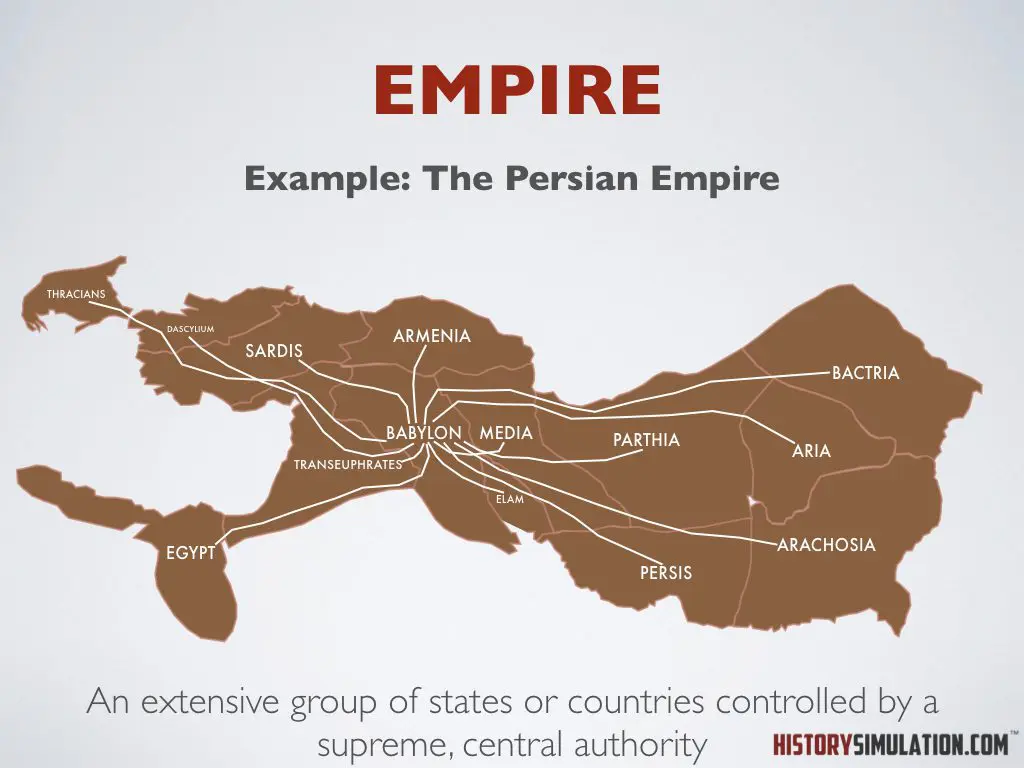
Empire: An extensive group of states or countries controlled by a supreme, central authority.

Fascism: Political philosophy that exalts nation and often race above the individual and is led by an authoritarian government.
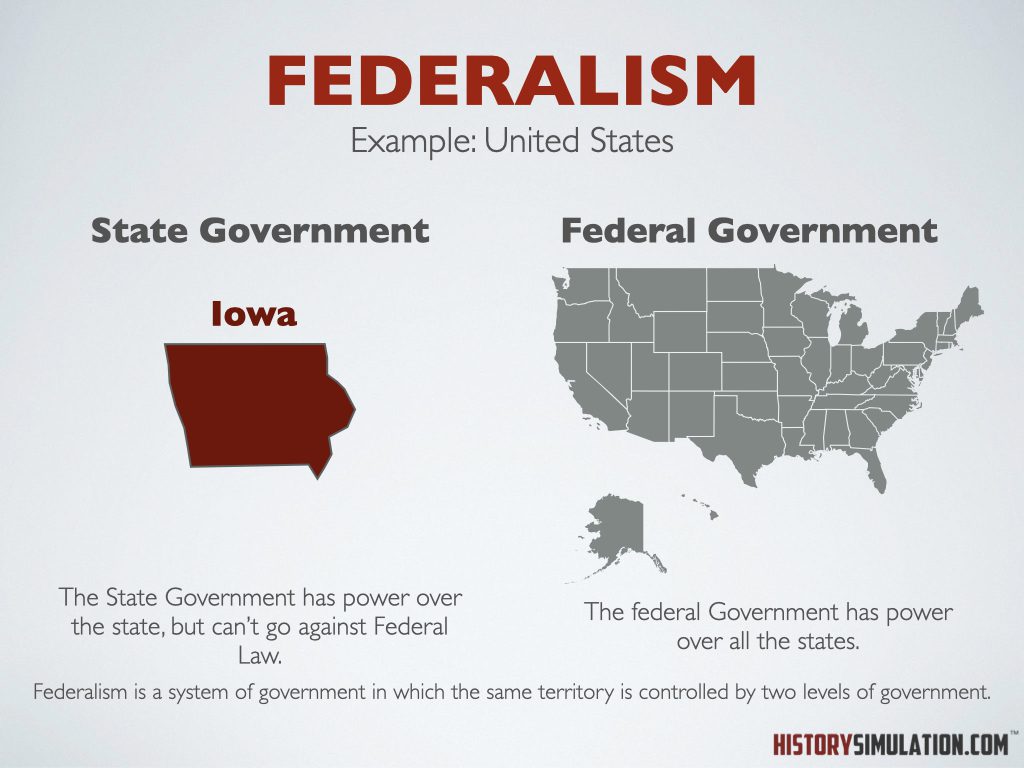
Federalism: Federalism is a system of government in which the same territory is controlled by two levels of government.
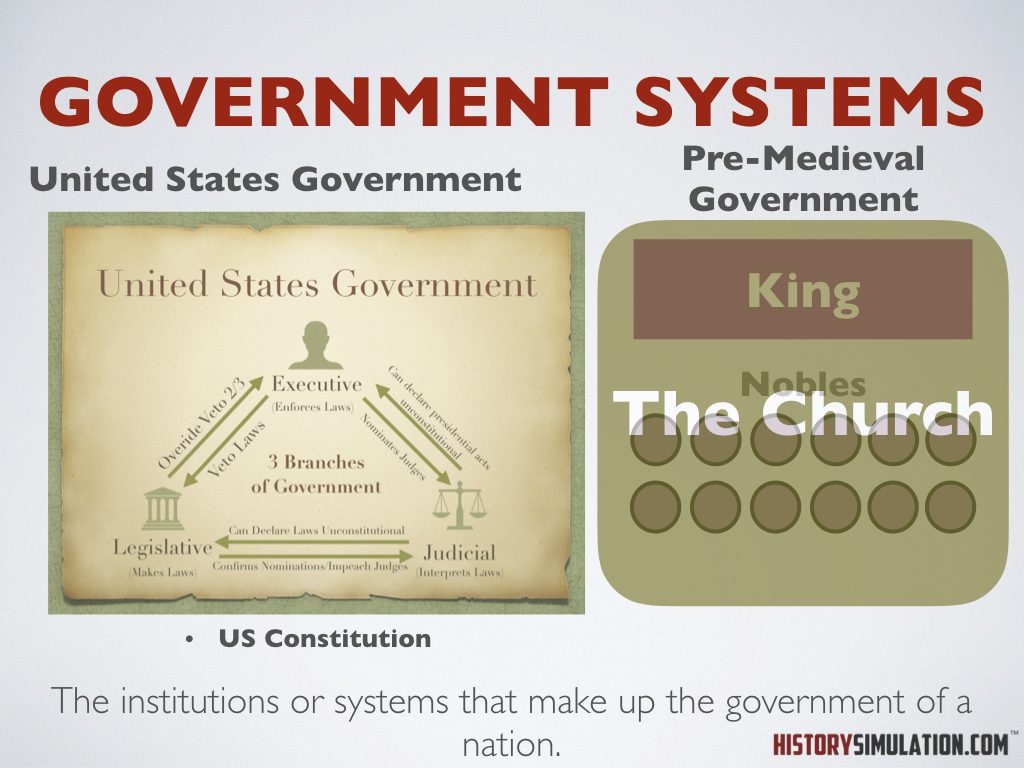
Government Systems: The institutions or systems which make up the government of a nation.
Example Video
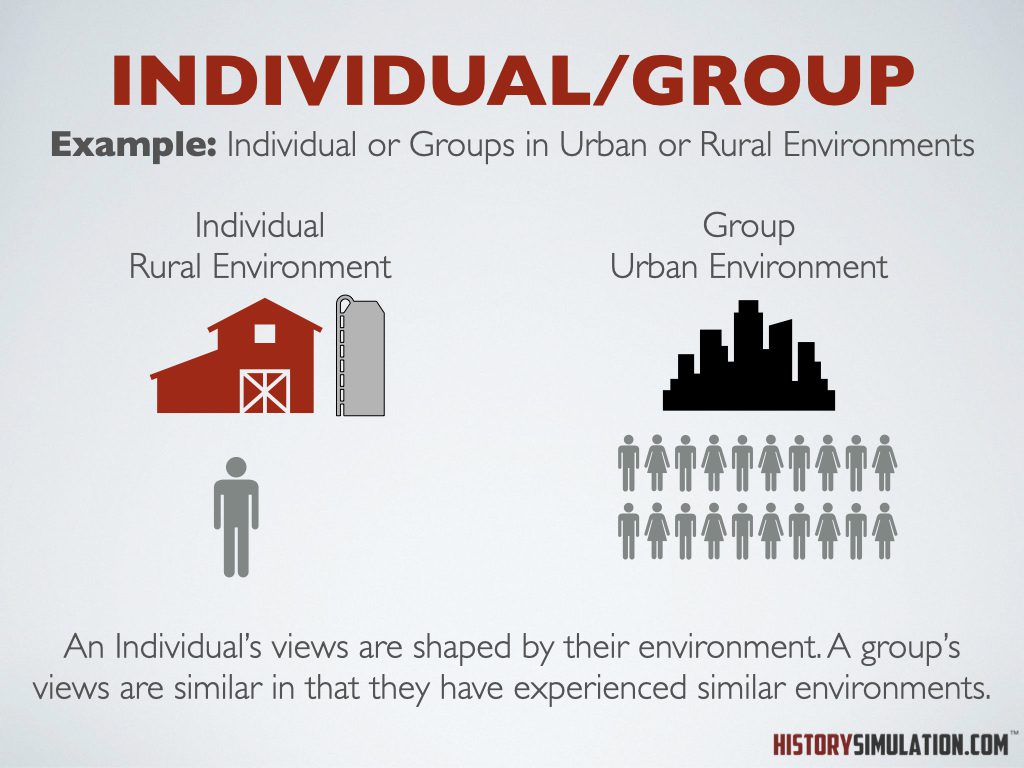
Individual/Group: An Individual’s views are shaped by their environment. A group’s views are similar in that they have experienced similar environments.

Institutions: A society or organization founded for a religious, educational, social, or similar purpose.

Law & Regulation: Law: a system of rules created and enforced through social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior Regulation: the act or process of controlling by rule or restriction

Leadership: To be responsible for guiding a group of people or nation.
Example Video

Nation-State: Nation: Homogeneous group of people (of the same nationality) State: Political organization that has sovereignty (makes their own decisions with no higher authority to answer to).

Principles: A fundamental truth or proposition that serves a s a foundation for a system of belief or behavior or for a chain of reasoning.

Justice: The process or result of using laws to fairly judge and punish crimes and criminals.

Politics: The activities associated with the governance of a country or other area, especially the debate or conflict among individuals or parties having or hoping to achieve power.

Power: The ability to influence the behavior of others with or without resistance.
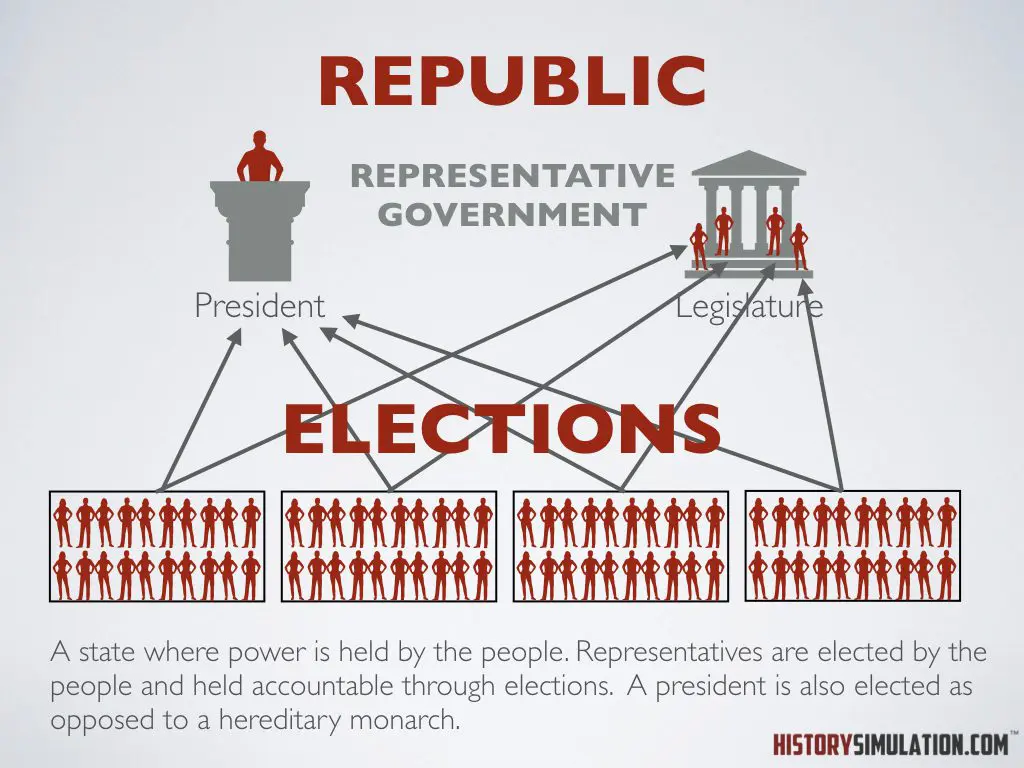
Republic: A state where power is held by the people. Representatives are elected by the people and held accountable through elections. A president is also elected as opposed to a hereditary monarch.

Rights and Responsibilities: A right is a choice to make your own opinion and entitlement to things such as education, religion and freedom of speech. Responsibilities are duties or something an individual should do such as following the law and rules.
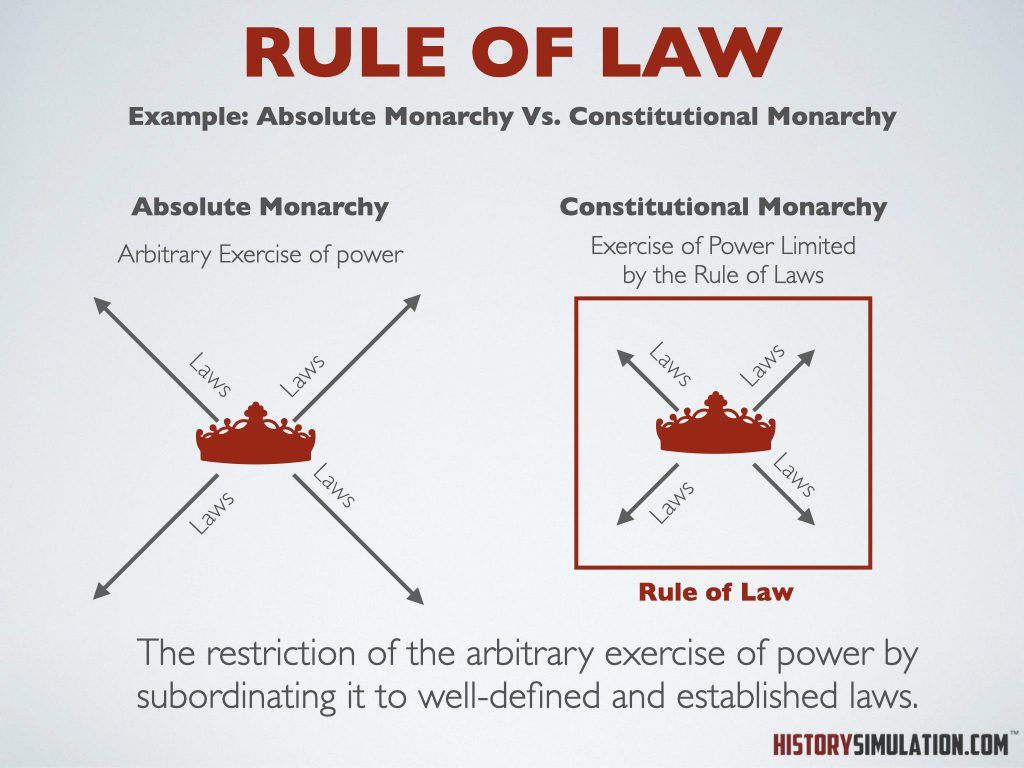
Rule of Law: The restriction of the arbitrary exercise of power by subordinating it to well-defined and established laws.
Socialism: A way of organizing society where the government owns part of the means of production and directs the economy.

Sovereignty: To have supreme authority within a territory.

Totalitarianism: Government control of all aspects of public and private life.
Example Video
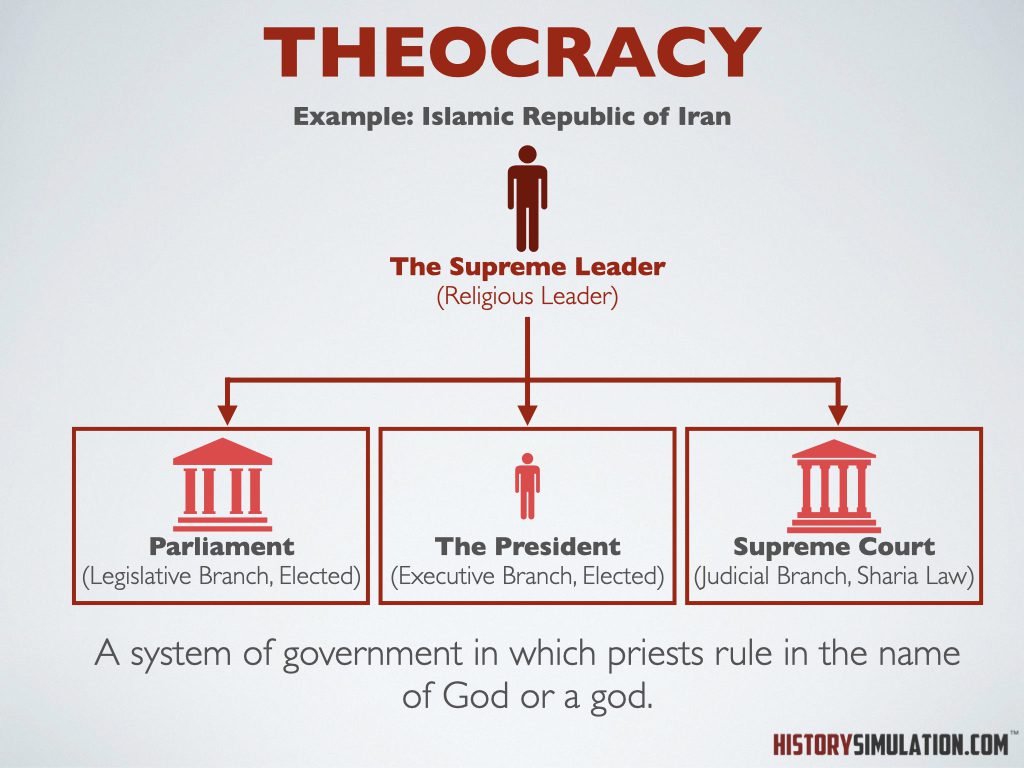
Theocracy: Is a form of government in which a deity is recognized as the supreme authority and government/law is based on religion.
Economics Concepts
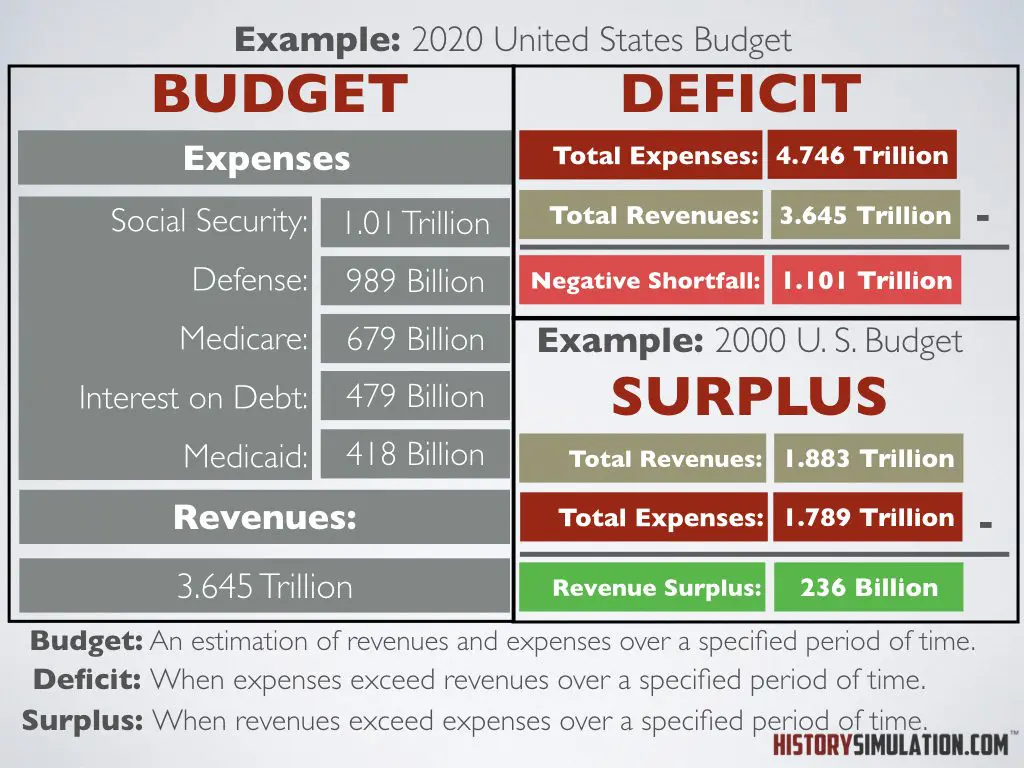
Budget: An estimation of revenues and expenses over a specified period of time.
Surplus: When revenues exceed expenses over s specified period of time.
Deficit: When expenses exceed revenues over a specified period of time.
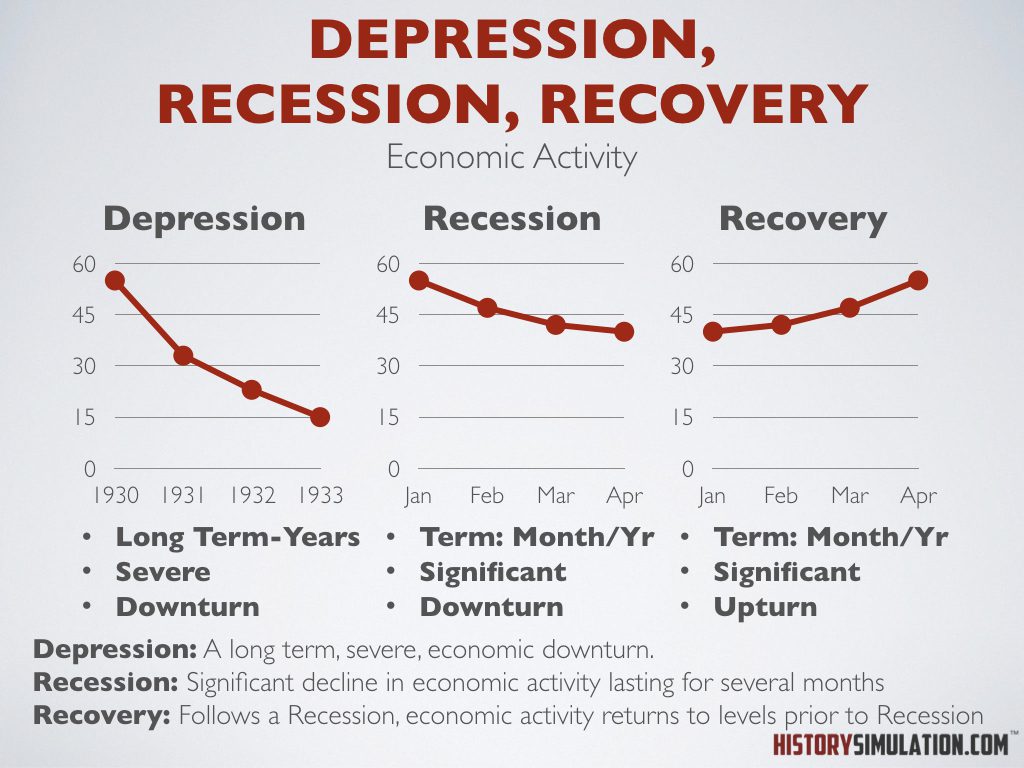
Depression, Recession, Recovery:
Depression: A long term, severe, economic downturn.
Recession: Significant decline in economic activity lasting for several months
Recovery: Follows a Recession, economy economic activity returns to levels prior to Recession
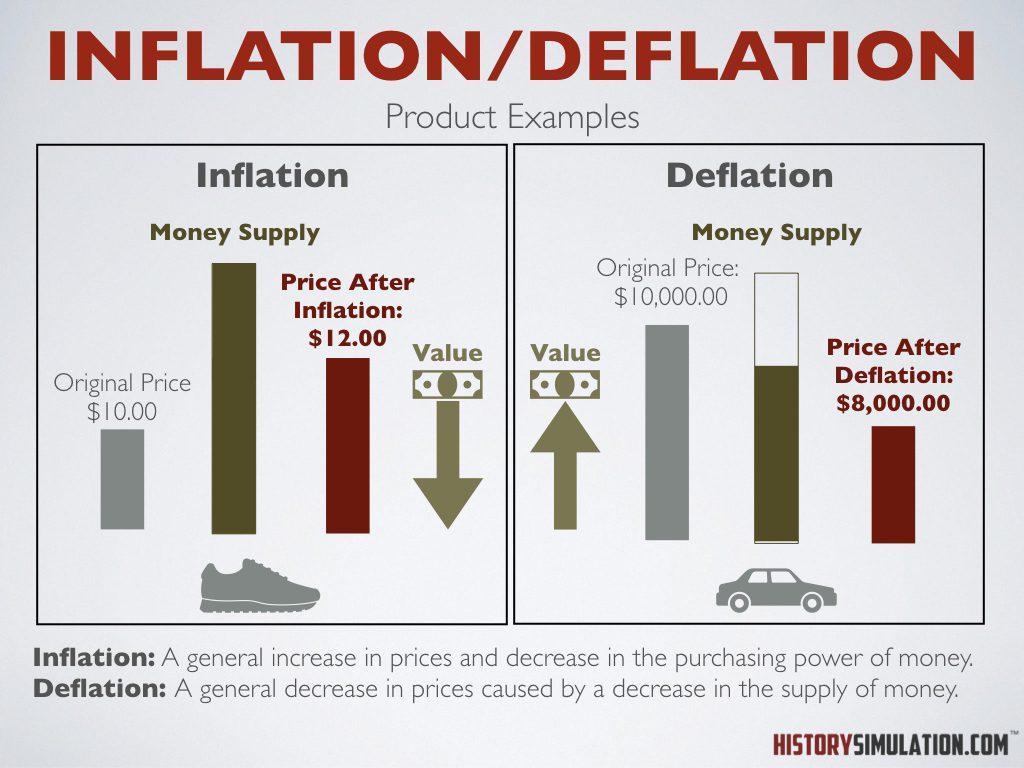
Inflation: A general increase in prices and decrease in the purchasing power of money.
Deflation: A general decrease in prices caused by a decrease in the supply of money.
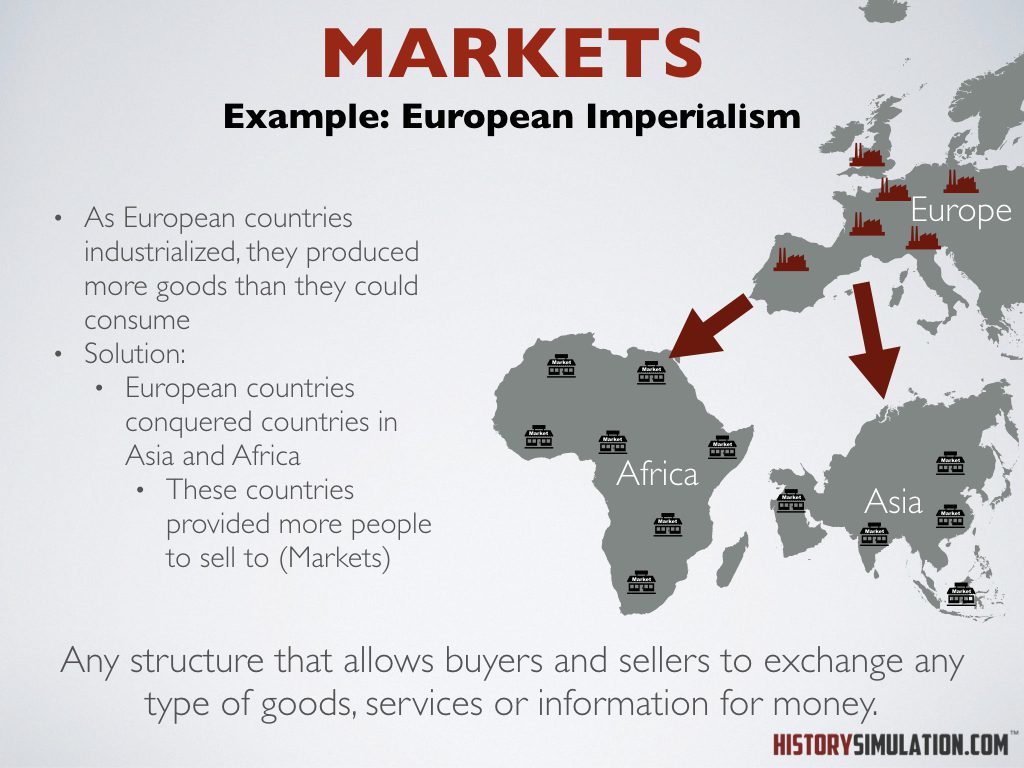
Markets: Any structure that allows buyers and sellers to exchange any type of goods, services or information for money.
Example Video

Natural Resources: Materials or substances that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain.

Supply & Demand: Supply- Quantity of a resource available, Demand- How great the need for the resource= Value.
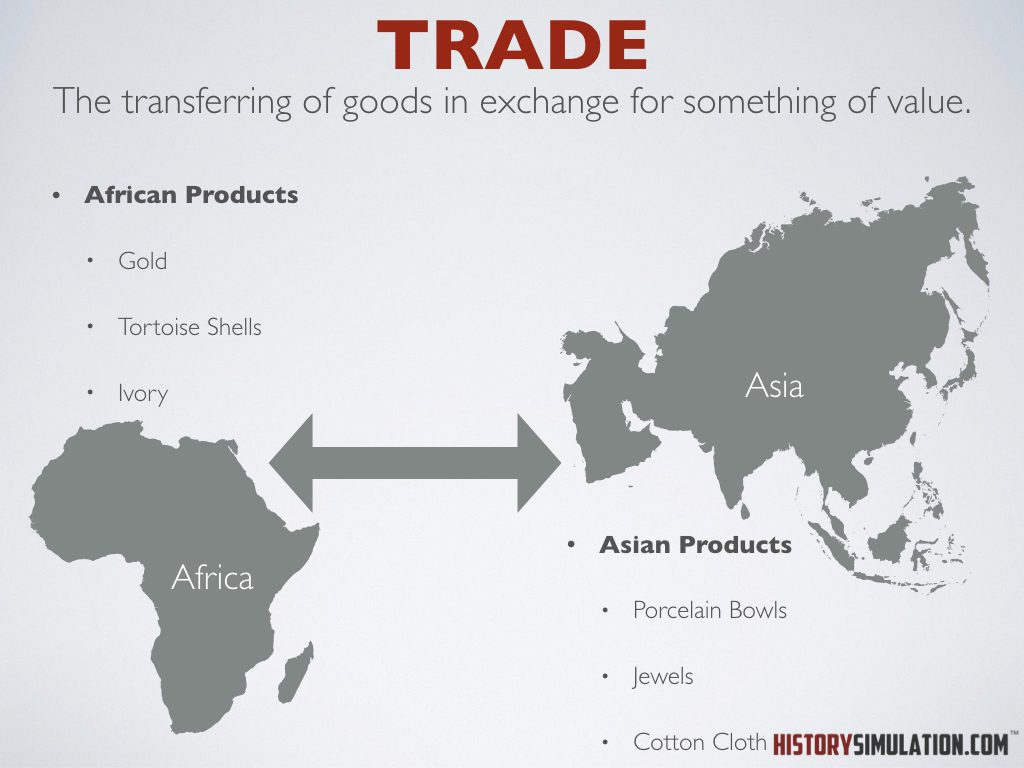
Trade: The transferring of goods in exchange for something of value. Ex. Money

Value: The importance, worth or usefulness of something.