World War 1 Map Activity and Other Teaching Resources
CREATE AN ENGAGING CLASSROOM WITH OUR INTERACTIVE, WORLD WAR 1 SIMULATION
If you are a history teacher, then you understand the importance of imparting the knowledge of historical events to your students. However, like many teachers, you are probably always looking for ways that you can incorporate new and exciting resources into your lesson plans.
If you are getting ready to teach about World War 1, you may be interested in a WW1 map activity that can help your students learn more about geography and history during the early 1900s. Read on to learn about HistorySimulation.com’s World War 1 map activity and other teaching resources.
Interactive Simulations
As a teacher, you know how hard it can be to get your students engaged in lessons. You might hear students complain about why they have to learn about history or how they are supposed to remember all the names, dates, and events in history.
An interactive simulation can help with this. Physical activities in the classroom often bridge the gap in students’ minds from listening to abstract lectures to actually engaging and retaining the material being taught.
World War 1 is a major event in world history, and students need to understand the events leading up to the war, as well as the events that took place during and after the war.
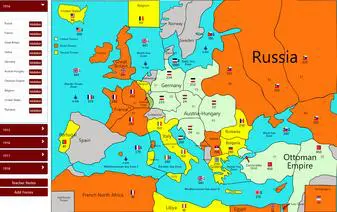
Some students may benefit from seeing the map of the world during this time and the color-coded countries, indicating the Allies from the Central Powers. Other students will benefit from the presentations that are included in the World War 1 Activity Bundle that detail the points before, during, and after the war.
Whether you teach in a private or public school or you homeschool your own children, WW1 map activities can be helpful to further your students’ understanding of this important part of history. For more information about our World War 1 map activity and other World War 1 resources, contact us at (515) 689-3960, or visit our resources page.
Are you looking for an interactive and engaging World War 1 Simulation for the classroom? Instead of lecturing to students about the Great War, engage students with this interactive activity.
Objectives
-Background of the countries involved in the war.
-The role alliances played in drawing multiple countries into the conflict.
-How Mobilization escalated tensions in Europe
-The affects of fighting a two front war.
-The advantage of the Allies Navy
-Students will develop a sense of Nationalism for their countries.
Online Learning Ready! We have created new systems, that will allow the teacher and students to be at their homes and conduct the simulation efficiently. Access to these tools are included. With ever changing conditions for our schools, having an online option gives the teacher and students great flexibility!


The Sequence of the Game
1913 Day 1
On day one of the simulation, the teacher introduces the simulation and goes through the Student Orientation Video or uses the Power Point / Keynote Presentations.
Next, the teacher will read and explain the following documents:
-Student Overview
-World Situation Summary
Then the teacher announces a "News Flash" coming across the wire: The Archduke of Austria-Hungary and his wife have been assassinated in Sarajevo!
Tensions begin to mount as the teacher directs the leaders of Austria-Hungary and Serbia to write speeches that will be read at the beginning of the next class (1914). The remainder of the period sees a flood of negotiations and diplomacy as leaders of the alliances meet and discuss the crisis.
1914 Day 2
Speeches
On day two, Austria-Hungary and Serbia start the class by reading their speeches in relation to the assassination of the Archduke of Austria-Hungary.
Mobilization
Next, the teacher asks if any countries would like to mobilize their armies. As students begin to raise their hands they take note of whether their neighbors are mobilizing or not and they can see each country's armies getting bigger on the map.
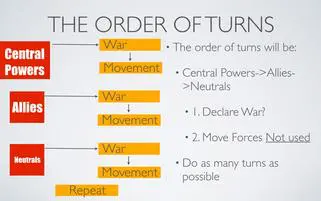
WAR!
Negotiations among and between the alliances start to get more intense. The Central Powers go first and so it's up to them to declare war or move their armies into position. After they have finished all of their battles they will go into movement. This is where you can move any army or navy forces you did not use during the war phase.
Transition To a Student Led Activity
1914-1918 Day 2-6
At this point, you are managing the map and students are driving the simulation through their objectives
Your students will take the roles of Woodrow Wilson, David Lloyd George, Kaiser Wilhelm II, Tsar Nicholas and many others. Most importantly, your students will get excited about The Great War and want to learn more!
- Form Alliances
- Conduct Diplomacy
- Negotiate Deals
- Strategic Thinking
- Problem Solve
- Critical Thinking
Click To Download
Try Our Online Demo:
World War 1 Games Online Demo
Email Login: [email protected] (Not an email)
Password: demo123
Tutorials
WW1 Simulation Preview
Student Simulation Tutorial
Online Teacher Tutorial
WWI Products & Information
Additional Information
National Standards
Era 8- A half century of crisis and achievement, 1900-1945
World History Content Standards
Standard 2: The causes and global consequences of World War I
Standard 2A: The student understands the causes of World War I
Therefore, the student is able to:
Analyze the relative importance of economic and political rivalries, ethnic and ideological conflicts, militarism, and imperialism as underlying causes of the war. (analyze multiple causation)
Analyze the precipitating causes of the war and the factors that produced military stalemate. (analyze cause-and-effect relationships)
Standard 2B: The student understands the global scope, outcome, and human costs of the war
Therefore, the student is able to:
Describe the major turning points of the war and the principal theaters of conflict in Europe, the Middle East, Sub-Saharan Africa, East Asia, and the South Pacific.
Analyze the role of nationalism and propaganda in mobilizing civilian populations in support of "total war". (Examine the influence of ideas)
Explain how massive industrial production and innovations in military technology affected strategy, tactics, and the scale and duration of the war. (Analyze cause and effect relationships)
Analyze how the Russian Revolution and the entry of the United States affected the course and the outcome of the war. (Analyze cause and effect relationships).